Introduction: Laser Therapy vs. CO2 Cryotherapy Overview
Pain relief and tissue recovery are at the forefront of modern medicine, with various treatment methods available. Laser therapy and CO2 cryotherapy are two of the most advanced modalities that are gaining popularity for their non-invasive and effective approaches.
What is Laser Therapy?
Laser therapy, especifically Class IV laser therapy, uses focused light energy to treat various conditions, including musculoskeletal pain, inflammation, and tissue damage. The laser light penetrates the skin and is absorbed by tissues, leading to increased cellular activity, enhanced blood flow, and reduced pain and inflammation. The photobiomodulation effect is the key to its healing capabilities, helping to stimulate cell regeneration, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue repair.
What is CO2 Cryotherapy?
CO2 cryotherapy, commonly known as carbon dioxide cryotherapy, involves the use of cold CO2 gas applied to targeted areas of the body. The cooling effect induces vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels), which reduces swelling, inflammation, and pain. In addition, the thermal shock response from rapid temperature change boosts circulation and stimulates cellular recovery. It’s commonly used in sports recovery and to alleviate inflammation or pain in muscles and joints.
Purpose of This Comparison
While both therapies offer powerful benefits, they differ in their mechanisms, speed of recovery, and applications. This article will dive deep into each therapy’s working principles, benefits, potential drawbacks, and ultimately, help you decide which treatment might be the best option for your specific needs.
Laser Therapy and Its Hot Mechanism
Laser therapy, especially Class IV laser therapy, uses light energy to create heat within tissues, promoting healing, reducing inflammation, and providing pain relief.
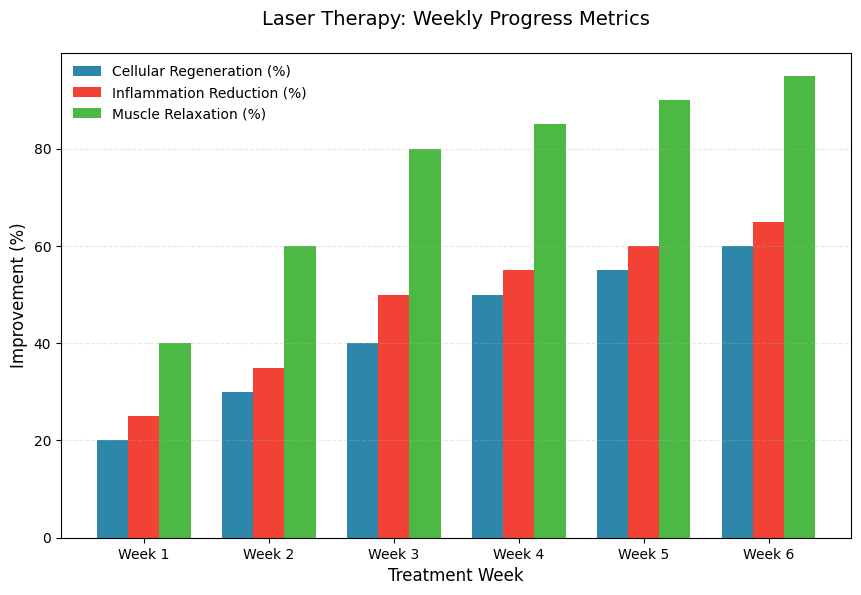
Heat Production and Absorption
When the laser light is directed at the skin and underlying tissues, it penetrates the surface layers and is absorbed by the cells. The energy from the laser is converted into heat within the tissue, primarily at the cellular level, particularly in the mitochondria. This absorption increases the activity of cellular metabolism and accelerates the natural healing process. The specific wavelengths used in laser therapy (usually 810nm or 980nm) are optimized to reach deep tissue layers and deliver therapeutic results effectively.
Therapeutic Heat and Increased Blood Flow
The heat generated by the laser triggers vasodilation (the expansion of blood vessels), which enhances blood circulation in the treated area. Improved circulation delivers more oxygen and nutrients to damaged tissues and removes waste products, further supporting the body’s ability to repair itself. Increased blood flow also facilitates the transport of immune cells, which are essential for fighting infection and promoting tissue regeneration. This mechanism is particularly beneficial in managing chronic injuries or inflammation, where the body’s natural healing process is sluggish.
Heat-Induced Pain Relief
Heat plays a critical role in pain relief during laser therapy. When tissues are heated, the nociceptors (pain receptors) within the skin and muscles are less likely to transmit pain signals to the brain. Moreover, the endorphins released during the treatment serve as the body’s natural analgesics, providing a secondary pain-relieving effect. By calming the nerve endings and reducing the intensity of pain signals, laser therapy offers long-term relief from conditions like arthritis, tendonitis, and muscle strains.
Heat and Collagen Production for Tissue Repair
Laser therapy is particularly beneficial for tissue regeneration, primarily because of its role in stimulating collagen production. Collagen is a crucial protein that helps in repairing damaged tissue and improving elasticity in muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The heat generated by the laser encourages the fibroblasts (cells that produce collagen) to work more efficiently, thus accelerating tissue repair. This effect is particularly helpful in recovering from injuries or surgeries where tissue healing is required.
CO2 Cryotherapy and Its Cooling Mechanism
In contrast to laser therapy’s use of heat, CO2 cryotherapy leverages the cooling properties of carbon dioxide to trigger healing responses and alleviate pain.
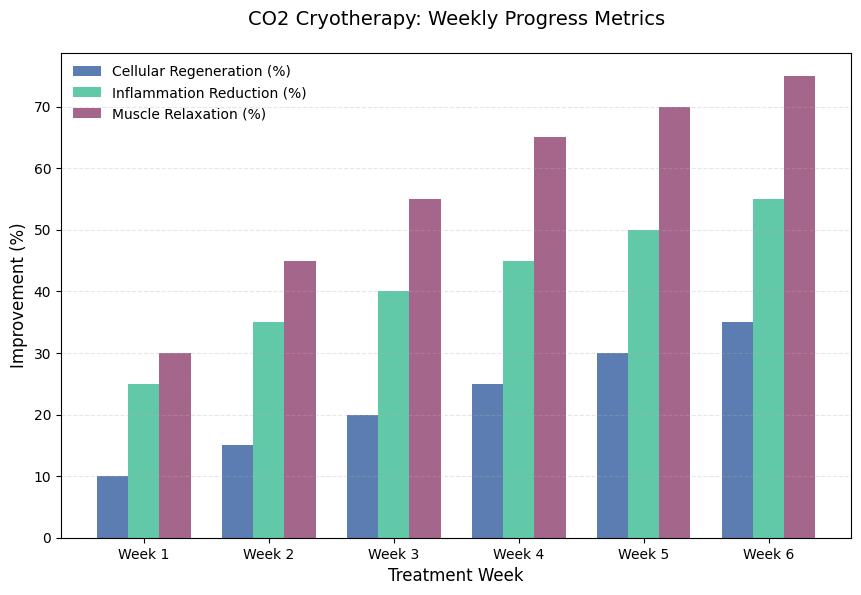
Cold-Induced Vasoconstriction
One of the main effects of CO2 cryotherapy is vasoconstriction, where blood vessels temporarily narrow due to exposure to cold. This constriction reduces the blood flow to the treated area, limiting the movement of inflammatory markers and reducing swelling. While blood flow is restricted, this cooling effect helps limit tissue damage and inflammation in areas of acute injury. When the cold treatment is removed, vasodilation (expansion of blood vessels) occurs, resulting in an increase in blood flow that brings nutrients and oxygen to the treated area, helping the body to recover.
Thermal Shock Response
The rapid temperature change from cold to warm generates a thermal shock response within the body. This reaction stimulates the nervous system, triggering the release of endorphins, which are natural painkillers. It also activates the body’s healing processes, including increased circulation and muscle relaxation. This sudden shift in temperature can help break down lactic acid buildup in muscles, improving muscle recovery after intense physical activity. The thermal shock response plays a key role in relieving muscle soreness and reducing muscle spasms.
Cold Temperature and Pain Relief
Cold therapy has been long recognized for its analgesic properties. The cooling effect from CO2 cryotherapy helps to numb the area being treated, reducing the transmission of pain signals to the brain. Additionally, the reduction in inflammation helps to relieve pain from injuries like sprains, strains, or post-surgical recovery. CO2 cryotherapy is particularly beneficial for acute injuries, where reducing swelling and pain quickly is a priority.
Key Differences Between Laser Therapy and CO2 Cryotherapy
Understanding the differences between laser therapy and CO2 cryotherapy is crucial for choosing the right treatment for your needs. These two therapies operate on fundamentally different mechanisms and have distinct effects on the body.
Treatment Mechanism
Laser therapy works by delivering light energy to targeted tissues. The light penetrates the skin and is absorbed by cells, converting into heat. This heat stimulates cellular activity, promotes blood flow, and helps in the healing of damaged tissues. Laser therapy is primarily used for chronic pain and deep tissue conditions, such as arthritis or muscle strains. The mechanism revolves around the photo-biomodulation process, which accelerates tissue regeneration. While CO2 cryotherapy utilizes cold carbon dioxide gas, applied to the skin via a device, to induce cooling of the affected area. This leads to vasoconstriction, a process where the blood vessels narrow, reducing inflammation and swelling. After the treatment, the blood vessels dilate, bringing oxygen and nutrients to the tissues for healing. The therapy works well for acute pain and swelling, often used for post-exercise recovery or to relieve acute injuries.
Speed and Duration of Results
When it comes to speed, CO2 cryotherapy offers immediate relief. The cooling effect is quickly, often providing a reduction in pain and swelling almost instantly after a session. However, the effects tend to be short-term, and multiple sessions are necessary to sustain the results. On the other hand, laser therapy requires multiple sessions for noticeable effects. The pain relief it provides is gradual and tends to improve over time as tissues heal and regenerate. Laser therapy can be a long-term solution for chronic conditions, but it may not offer immediate pain relief compared to cryotherapy.
Side Effects and Considerations
Both treatments are generally safe, but there are specific considerations for each. Laser therapy, while effective, can sometimes cause skin irritation or burns if applied improperly. It’s also important to note that laser therapy may not be suitable for acute injuries with significant swelling, as the heat could potentially worsen the condition during the early stages of recovery. CO2 cryotherapy is generally safe, but the cooling effects need to be carefully monitored to avoid frostbite or cold burns. It is not recommended for people with conditions like Raynaud’s disease or those with cold sensitivity, as extreme cold can exacerbate circulation issues.
Targeted Conditions
Both laser therapy and CO2 cryotherapy are highly effective for certain conditions, and knowing which therapy is best for your specific issue can greatly enhance the healing process.
Laser Therapy: Best for Chronic and Deep Tissue Conditions
Laser therapy excels in treating chronic pain and deep tissue injuries, including:
- Joint-Related Injuries: Laser therapy helps reduce pain and inflammation, stimulate joint healing, and improve flexibility in conditions.
- Muscle Strains and Sprains: By promoting cell regeneration and tissue healing, laser therapy is effective for muscle tears and ligament injuries.
- Tendinitis: Chronic tendinitis, whether in the shoulder, elbow, or knee, benefits from laser therapy’s ability to stimulate collagen production, aiding in tendon healing.
- Back and Neck Pain: Laser therapy is particularly effective for lower back pain, sciatica, and neck pain by increasing circulation and reducing inflammation in the affected tissues.
- Post-Surgical Recovery: For patients recovering from surgery, laser therapy accelerates healing and reduces scar tissue formation.
CO2 Cryotherapy: Best for Acute Injuries and Inflammation
CO2 cryotherapy is most effective for acute conditions that require immediate relief and inflammation reduction:
- Sports Injuries: CO2 cryotherapy is commonly used for muscle soreness, bruising, sprains, and swelling caused by sports activities. Its cold-induced vasoconstriction quickly reduces inflammation and numbs pain.
- Post-Exercise Recovery: After intense physical exertion, CO2 cryotherapy helps athletes recover faster by reducing muscle fatigue, lactic acid buildup, and swelling.
- Acute Inflammation: For conditions like tendonitis, bursitis, and acute strains, cryotherapy helps to rapidly reduce swelling and pain.
- Headaches and Migraines: Cryotherapy is increasingly used for headaches, particularly migraines, where the cold sensation helps soothe the pain and may constrict the blood vessels that cause it.
- Skin Conditions: Cryotherapy has been used for cosmetic purposes such as wrinkle reduction, skin rejuvenation, and treating sunburns or skin lesions due to its ability to stimulate collagen production through cold exposure.
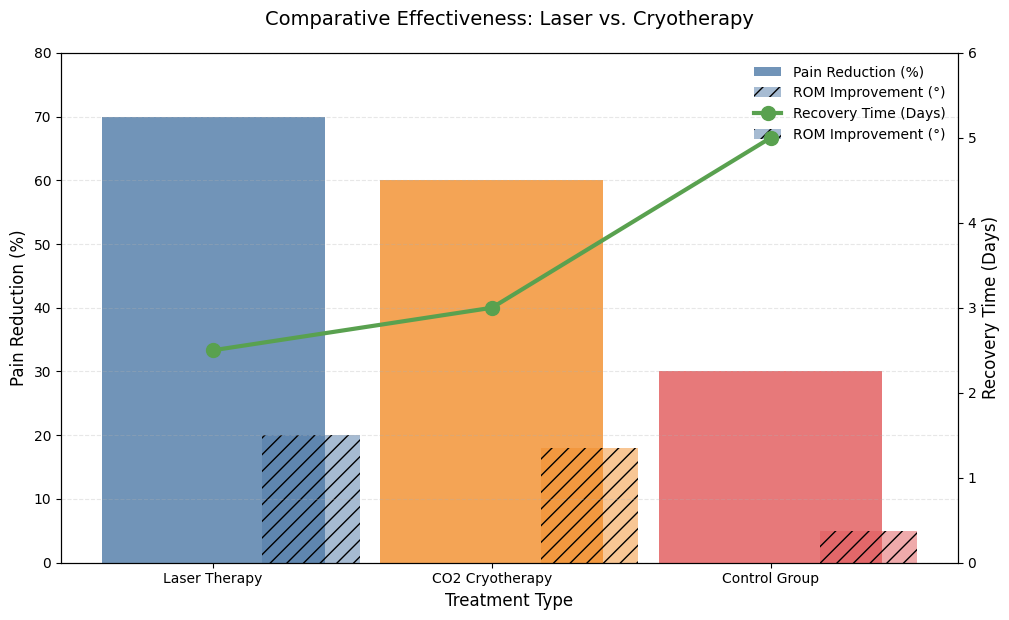
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Each Therapy
When choosing between laser therapy and CO2 cryotherapy, it’s important to consider the specific benefits and drawbacks of each treatment to determine which one suits your individual needs.
Benefits of Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a powerful tool for long-term tissue repair. Its ability to promote collagen production makes it highly effective for healing muscle strains, ligament injuries, and conditions like arthritis. The increased blood circulation helps oxygenate tissues, leading to faster recovery. One of the biggest advantages is that it is a non-invasive therapy with minimal downtime, allowing patients to return to their normal activities without significant disruptions. Laser therapy is also famous of its ability to treat deep tissue injuries, such as those found in the back, joints, and muscles, which makes it suitable for people with chronic conditions or long-term injuries.
Benefits of CO2 Cryotherapy
CO2 cryotherapy offers immediate pain relief and is especially effective for conditions with acute pain, such as muscle soreness, sprains, and swelling. It is commonly used in sports recovery, providing fast relief from intense physical exertion. Additionally, it is highly effective at reducing inflammation, making it ideal for conditions like tendonitis or post-surgical recovery. The therapy is non-invasive, and patients typically experience little to no downtime afterward, making it a convenient option for individuals with busy schedules or athletes looking for quick recovery methods.
Drawbacks of Laser Therapy
Despite its many benefits, laser therapy requires a commitment to multiple sessions for optimal results. For those seeking immediate pain relief, laser therapy may not provide the quick results needed, especially in cases of acute pain or fresh injuries. Additionally, heat may not always be suitable for certain injuries in the initial stages, as it could exacerbate inflammation. Laser therapy may also be limited by factors such as cost and accessibility, as it often requires specialized equipment and may not be as readily available as other treatments like cryotherapy.
Drawbacks of CO2 Cryotherapy
While CO2 cryotherapy provides fast relief, its effects tend to be temporary. For those with chronic pain or long-term conditions, the relief may not last, and multiple treatments are necessary to maintain effectiveness. Cryotherapy may not address the underlying causes of pain or inflammation, and it is often best for managing acute conditions rather than long-term healing. Another drawback is the risk of cold burns if the therapy is not administered properly. Skin sensitivity can also be a concern, especially for individuals with sensitive skin or underlying conditions that affect circulation.
Conclusion: Which Therapy is Right for You?
Ultimately, the decision between laser therapy and CO2 cryotherapy depends on the nature of your condition, your recovery goals, and your personal preferences. Each therapy offers unique advantages and has its place in treating pain, inflammation, and injury.
When to Choose Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is an ideal choice if you are dealing with chronic pain or deep tissue injuries, such as those from arthritis, back pain, or tendonitis. It is also highly effective for long-term healing and tissue regeneration. If you’re seeking a solution that supports tissue recovery and provides lasting benefits over time, laser therapy might be the best option for you.
When to Choose CO2 Cryotherapy
CO2 cryotherapy is the go-to treatment if you need quick pain relief and swelling reduction for acute injuries or sports recovery. It’s perfect for athletes or individuals who need fast muscle recovery after intense physical activity. If your focus is on short-term relief and a fast recovery, cryotherapy might be the ideal therapy.
Final Recommendation: Which Therapy Fits Your Needs?
Both laser therapy and CO2 cryotherapy have distinct advantages depending on the severity and duration of your symptoms. If you are looking for long-term relief and addressing deeper issues, laser therapy is the more suitable option. However, if your primary goal is immediate pain relief and reducing swelling, CO2 cryotherapy is the optimal choice. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help tailor the right treatment plan for you, ensuring that your chosen therapy aligns with your recovery needs.
FAQs
Q1. What is the difference between laser therapy and CO2 cryotherapy?
Laser therapy uses focused light energy to penetrate deep into tissues, promoting healing and pain relief, while CO2 cryotherapy applies extreme cold to the body to reduce inflammation, numb pain, and accelerate recovery from acute injuries.
Q2. How long does each therapy take to show results?
Results from laser therapy are often visible within a few sessions, especially for chronic conditions like arthritis or muscle pain. On the other hand, CO2 cryotherapy typically provides immediate relief from pain and inflammation, with noticeable benefits after a single treatment, particularly for acute injuries.
Q3. Are there any side effects to laser therapy or CO2 cryotherapy?
Laser therapy has minimal side effects, usually limited to mild skin irritation or discomfort in some cases. CO2 cryotherapy may cause temporary redness or numbness in the treated area but is generally well tolerated. Long-term side effects for both therapies are rare.
Q4. Can laser therapy and CO2 cryotherapy be combined?
Yes, combining both therapies can be beneficial for some individuals. For instance, CO2 cryotherapy can be used for acute inflammation and pain relief, followed by laser therapy to promote healing and tissue regeneration in chronic conditions.
Q5. How many sessions of laser therapy or cryotherapy are necessary for effective results?
For laser therapy, most patients require around 6 to 12 sessions for chronic conditions, while acute injuries may require fewer treatments. CO2 cryotherapy is typically effective with 1 to 3 sessions for immediate pain relief and inflammation reduction, though ongoing treatments may be necessary for chronic conditions.
Q6. Is laser therapy painful?
No, laser therapy is generally painless. Patients may feel a mild warmth or tingling sensation during the treatment, but it is usually comfortable and non-invasive.
References
Effect of Cold and Heat Therapies on Pain Relief in Patients with Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness: A Network Meta-Analysis:



