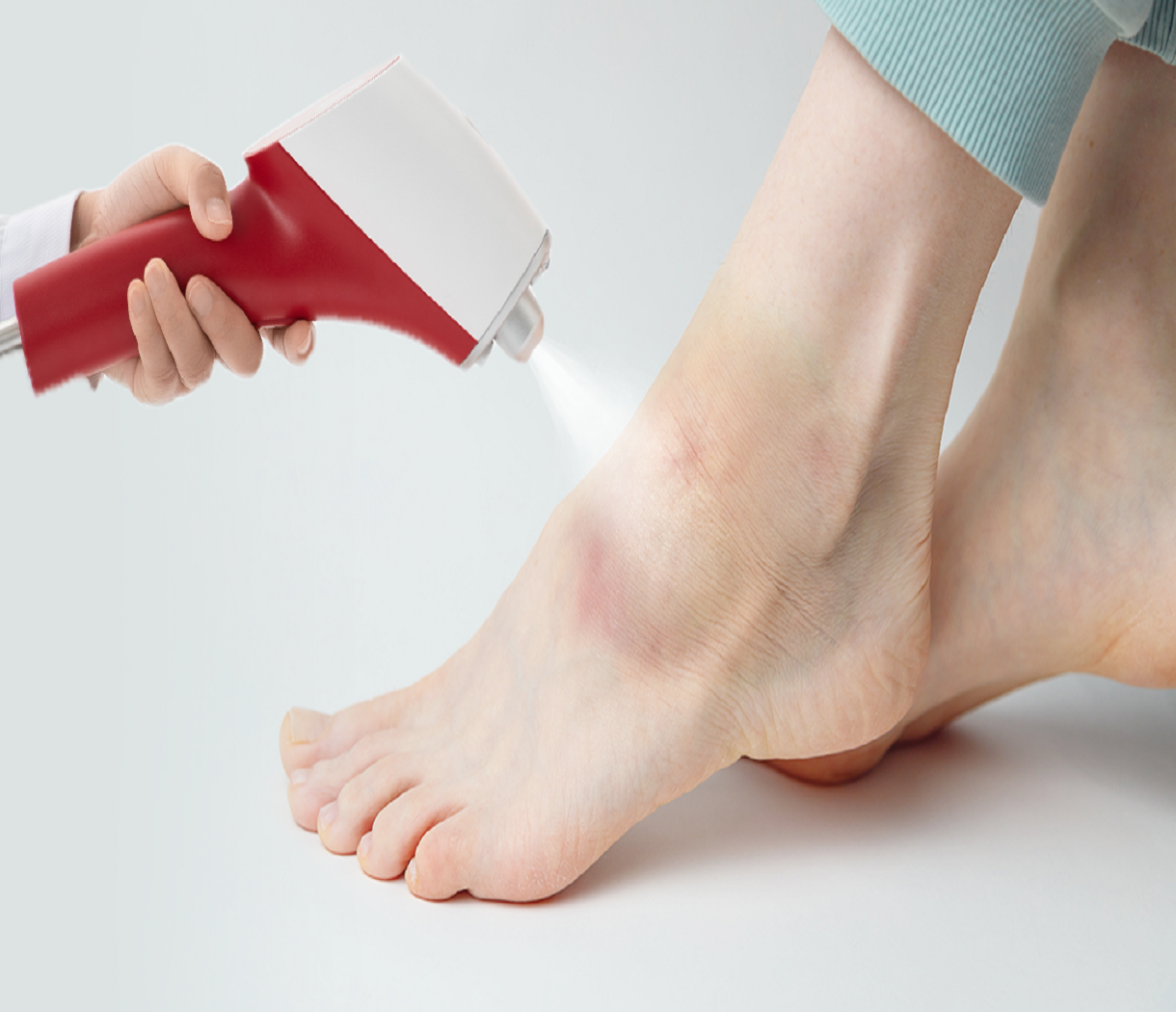
Introduction to CO₂ Cryotherapy
CO₂ cryotherapy involves the application of carbon dioxide gas at extremely low temperatures (-78°C) to targeted areas, inducing rapid cooling and promoting healing. This method has gained attention for its efficacy in reducing pain and inflammation associated with various injuries, including hematomas.
The Old School Way: Ice vs. Cryotherapy
Traditionally, ice packs have been the standard treatment for managing soft tissue injuries. While effective in surface-level cooling, ice therapy has limitations:
- Depth of Penetration: Ice primarily affects superficial tissues and may not adequately reach deeper hematomas.
- Application Time: Achieving therapeutic effects with ice requires prolonged application, which can lead to discomfort and potential skin damage.
In contrast, CO₂ cryotherapy delivers rapid and deep cooling, addressing these shortcomings effectively. CO₂ can cool the skin to 2-4°C within 5-10 seconds, allowing for a recovery time of under 10seconds with no cellular damage.
The Concept of “Cooling” as Healing
The therapeutic application of cold, known as cryotherapy, leverages the body’s natural responses to reduced temperatures:
- Vasoconstriction: Immediate narrowing of blood vessels reduces blood flow, minimizing swelling and bleeding.
- Analgesia: Cold temperatures numb nerve endings, providing pain relief.
- Reduced Metabolic Rate: Lower temperatures slow cellular metabolism, decreasing the risk of secondary tissue damage.
These effects collectively create an optimal environment for tissue repair and recovery.
Understanding Hematomas: Why They Need Special Treatment
A hematoma is a localized collection of blood outside the blood vessels, usually in liquid form within the tissue. It occurs due to vessel damage, leading to blood leakage and clot formation.
Hematomas: More Than Just Bruises
Unlike simple bruises, hematomas involve significant blood accumulation, causing:
- Increased Pressure: Accumulated blood can compress surrounding tissues, leading to pain and restricted movement.
- Inflammatory Response: The body reacts to the injury by initiating inflammation, which, if excessive, can hinder healing.
Effective management is crucial to prevent complications such as fibrosis or calcification.
The Challenge: Persistent Inflammation and Swelling
Persistent inflammation in hematomas can lead to:
- Delayed Healing: Continuous swelling hampers nutrient and oxygen delivery to the affected area.
- Pain and Discomfort: Ongoing inflammation keeps pain receptors activated, prolonging discomfort.
Addressing these challenges requires interventions that can effectively reduce inflammation and promote efficient healing.
How CO₂ Cryotherapy Works
CO₂ cryotherapy employs pressurized carbon dioxide gas at approximately -78°C to induce rapid cooling of the targeted area. This process, known as thermal shock, triggers several physiological responses beneficial for hematoma treatment.
Targeting the Source: Cryotherapy for Deep Tissue Impact
The high-pressure application allows CO₂ to penetrate deeper tissues compared to traditional ice therapy. This deep tissue impact is crucial for effectively treating hematomas located beneath the skin’s surface.
- Rapid Cooling: Skin temperature can drop to 2-4°C within 30-60 seconds, reaching therapeutic levels swiftly.
- Localized Treatment: The precision of CO₂ application ensures that only the affected area is treated, preserving surrounding healthy tissues.
Supercharging Blood Flow: Cryotherapy’s Role in Circulation
Following the initial vasoconstriction, a rebound vasodilation occurs, enhancing blood flow to the area. This process:
- Facilitates Removal of Waste Products: Increased circulation helps clear out cellular debris from the injury site.
- Delivers Oxygen and Nutrients: Enhanced blood flow supplies essential components for tissue repair.
This dynamic modulation of blood flow accelerates the healing process.
Minimizing Pain Signals: Numbing with Precision
The rapid cooling effect of CO₂ cryotherapy numbs the area by reducing nerve conduction velocity. This leads to immediate pain relief without the need for pharmaceutical interventions, allowing patients to engage in rehabilitation exercises sooner.
The Science of CO₂ Cryotherapy for Hematomas
CO₂ cryotherapy is grounded in fundamental thermodynamics and cellular biology. By rapidly cooling tissue, it induces physiological responses that accelerate hematoma resolution.
The Mechanisms of Cold: Understanding Cryo’s Effect on Cells
Vasoconstriction and Vasodilation Cycle:
- Initial vasoconstriction reduces blood flow, limiting further hemorrhaging and controlling inflammation.
- Subsequent vasodilation enhances nutrient delivery and waste removal, expediting tissue repair.
Cellular Metabolism Reduction:
- Cryotherapy slows metabolic activity, decreasing oxygen demand and reducing oxidative stress, which mitigates secondary tissue damage.
Neural Modulation and Pain Reduction:
- Cold exposure inhibits nociceptor activation, disrupting pain signaling at the peripheral and central nervous system levels.
Enhanced Leukocyte Activity:
- Studies indicate that cryotherapy modulates leukocyte function, optimizing immune responses crucial for clearing dead cells and promoting regeneration.
Cellular Effects of CO₂ Cryotherapy on Hematomas
| Mechanism | Effect on Cells | Benefit for Hematomas |
| Vasoconstriction | Limits blood flow | Reduces swelling |
| Vasodilation | Improves circulation | Speeds up recovery |
| Metabolic slowdown | Decreases oxygen demand | Minimizes tissue damage |
| Nerve inhibition | Blocks pain receptors | Provides analgesia |
| Leukocyte modulation | Enhances immune response | Clears damaged tissue efficiently |
The Thermodynamic Effect: Cooling to Heal Faster
CO₂ cryotherapy leverages thermodynamic cooling, impacting tissue recovery at multiple levels:
Rapid Thermal Shock (-78°C, 5-10s Application): Quick skin cooling (2-4°C within 30-60s) causes an immediate biological response.
Cryo-induced Microcirculation Boost: Post-cryotherapy, blood flow increases, flushing out stagnated fluids and promoting capillary repair.
Controlled Inflammation Modulation: Unlike ice therapy, which may induce prolonged vasoconstriction, CO₂ cryotherapy balances inflammatory responses, preventing fibrosis or chronic stiffness.
Why CO₂ Cryotherapy Is Gaining Popularity in Hematoma Treatment
The advantages of CO₂ cryotherapy make it an attractive treatment for hematomas, especially among high-performance individuals and rehabilitation specialists.
Athletes and Active Individuals: CO₂ Cryotherapy for Speedy Recovery
Elite athletes incorporate cryotherapy due to:
Shorter Recovery Times: Case studies show that CO₂ cryotherapy reduces hematoma healing times by up to 40% compared to conventional R.I.C.E. therapy.
Enhanced Performance Maintenance: Faster pain relief allows for earlier return-to-play protocols, minimizing downtime.
Reduced Dependence on NSAIDs: With natural analgesic effects, athletes reduce reliance on anti-inflammatory medications, avoiding gastrointestinal and renal complications.
Real Patients, Real Results: Testimonials That Speak Volumes

Real patient experiences provide the best insight into the effectiveness of CO₂ cryotherapy for treating hematomas. Here’s a glimpse of how this treatment is transforming recovery:
John, an amateur athlete, shared: “After a deep bruise from a soccer match, the swelling was unbearable. One CO₂ cryotherapy session gave me immediate relief. The swelling reduced fast, and I was back to training in days. I was skeptical at first, but now I swear by it!”
Mary, an office worker, experienced: “After a fall while hiking, I developed a painful hematoma on my thigh. CO₂ cryotherapy gave me instant pain relief, and the swelling went down immediately. The bruise healed much faster than I expected.”
Alex, a professional rugby player, said: “Injuries are part of the job. CO₂ cryotherapy helped me recover from a calf hematoma in record time. The pain relief was almost instant, and I was back on the field quicker than ever.”
Susan, a retired teacher, commented: “Bruises take forever to heal at my age, and I hate painkillers. CO₂ cryotherapy sped up my recovery. My bruise disappeared in half the usual time.”
Mark, a weekend warrior, explained: “After a weekend of crossfit, I developed a hematoma on my arm. CO₂ cryotherapy reduced pain and swelling immediately. It was a game-changer in my recovery process!”
Why CO₂ Cryotherapy Works Better Than Others
CO₂ cryotherapy outperforms alternative treatments like ice therapy, compression therapy, and traditional cryogenic chambers due to:
Precision Cooling vs. Ice Therapy
Ice Therapy:
- Uncontrolled cooling → Risk of frostbite or inadequate penetration.
- Requires 20+ minutes per session, delaying rewarming benefits.
CO₂ Cryotherapy:
- Immediate effect (-78°C) with controlled delivery (5-10 seconds).
- Avoids overcooling risks while reaching deeper tissue.
CO₂ Cryotherapy vs. Traditional Cryo Chambers
Cryo Chambers (-110°C):
- Whole-body exposure → Less targeted, more generalized effects.
- Requires specialized facilities and higher costs.
CO₂ Cryotherapy (-78°C, localized):
- Portable, direct application for focused healing.
- More cost-effective for clinics and individuals.
Not Only for Hematomas, But Also…
CO₂ cryotherapy, known for its rapid cooling capabilities, extends its therapeutic benefits beyond hematoma treatment. Its efficacy in addressing various musculoskeletal and inflammatory conditions has been increasingly recognized.
Joint Inflammation and Sprains
Joint inflammation and sprains often result in pain, swelling, and reduced mobility. CO₂ cryotherapy delivers localized cold therapy at approximately -78°C for brief durations (5-10 seconds), inducing vasoconstriction that reduces blood flow to the affected area, thereby diminishing inflammation and edema. This process also numbs nerve endings, providing immediate pain relief. Such treatments have been associated with accelerated recovery times and improved joint function.
Muscle Strains and Soft Tissue Injuries
Muscle strains and soft tissue injuries benefit from CO₂ cryotherapy’s ability to rapidly decrease tissue temperature, leading to metabolic slowdown in the injured cells. This reduction in metabolic activity helps limit secondary tissue damage and promotes faster healing. The application of CO₂ at -78°C for 5-10 seconds can effectively penetrate deep into muscle tissues, providing relief from soreness and facilitating the repair process.
Post-Surgery Recovery
Post-operative recovery can be enhanced through CO₂ cryotherapy by minimizing pain and swelling at surgical sites. The therapy’s rapid cooling effect constricts blood vessels, reducing post-surgical bleeding and inflammation. Patients often report decreased reliance on analgesics and a more comfortable recovery period when CO₂ cryotherapy is incorporated into their post-operative care regimen.
Chronic Pain and Inflammation Disorders
Chronic conditions such as arthritis and tendinitis involve persistent inflammation and pain. Regular application of CO₂ cryotherapy can modulate inflammatory responses and provide analgesic effects, improving the quality of life for individuals with chronic pain disorders. The therapy’s ability to deliver targeted cold treatment makes it a valuable tool in managing long-term inflammatory conditions.
Common Questions About CO₂ Cryotherapy for Hematomas
Q1. Is CO₂ Cryotherapy Safe for All Ages?
Yes, CO₂ cryotherapy is generally safe for most age groups. However, individuals with conditions such as Raynaud’s disease, circulatory disorders, or hypersensitivity to cold should consult a healthcare provider before treatment. Children and elderly patients should undergo therapy under medical supervision to ensure safety.
Q2. Is CO₂ Cryotherapy Effective for Large Hematomas?
Yes, CO₂ cryotherapy can effectively treat large hematomas by reducing swelling and accelerating blood reabsorption. However, multiple sessions may be required, and combination treatments with compression therapy or physiotherapy might be recommended for optimal results.
Q3. Does CO₂ Cryotherapy Have Any Side Effects?
CO₂ cryotherapy is generally well tolerated. Temporary redness, numbness, or mild tingling at the treatment site may occur. In rare cases, overexposure to extreme cold may cause superficial frostbite or skin irritation, which is why treatment duration is carefully controlled.
Q4. Can CO₂ Cryotherapy Be Used on All Body Parts?
CO₂ cryotherapy can be used on most body areas, including limbs, joints, and soft tissues. However, caution is advised when applying it to highly sensitive areas like the face or areas with compromised circulation. A trained professional should assess whether it’s appropriate for specific injury sites.
Q5. Does CO₂ Cryotherapy Improve Athletic Performance?
Athletes use CO₂ cryotherapy not just for recovery but also for performance enhancement. By reducing muscle soreness, increasing blood flow, and decreasing inflammation, cryotherapy helps athletes maintain peak condition and reduce downtime from injuries.
References
Is it time to put traditional cold therapy in rehabilitation of soft-tissue injuries out to pasture?
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8173427
Effectiveness of carbon dioxide cryotherapy for the treatment of localized cutaneous leishmaniasis:
https://journals.plos.org/plosntds/article?id=10.1371/journal.pntd.0012741