Introduction to Instant CO₂ Cooling in Injury Care
The management of acute injuries has evolved significantly over the past decades, with innovative therapeutic modalities emerging to enhance patient outcomes and accelerate recovery. Among these advances, instant carbon dioxide (CO₂) cooling has established itself as a revolutionary approach to acute injury care, offering unprecedented precision and efficacy in therapeutic intervention.
Importance of Immediate Treatment in Acute Injuries
The golden hour principle in acute injury management emphasizes the critical importance of immediate intervention to optimize healing outcomes. Research demonstrates that the first few hours following tissue trauma are crucial for determining the extent of secondary injury and subsequent recovery trajectory. During this acute phase, inflammatory cascades, cellular metabolism, and vascular responses can either promote healing or exacerbate tissue damage. Immediate therapeutic intervention can significantly influence these processes, making the timing of treatment paramount in achieving optimal clinical outcomes and minimizing long-term complications.
What Is Instant CO₂ Cooling and How Does It Help Acute Injuries?
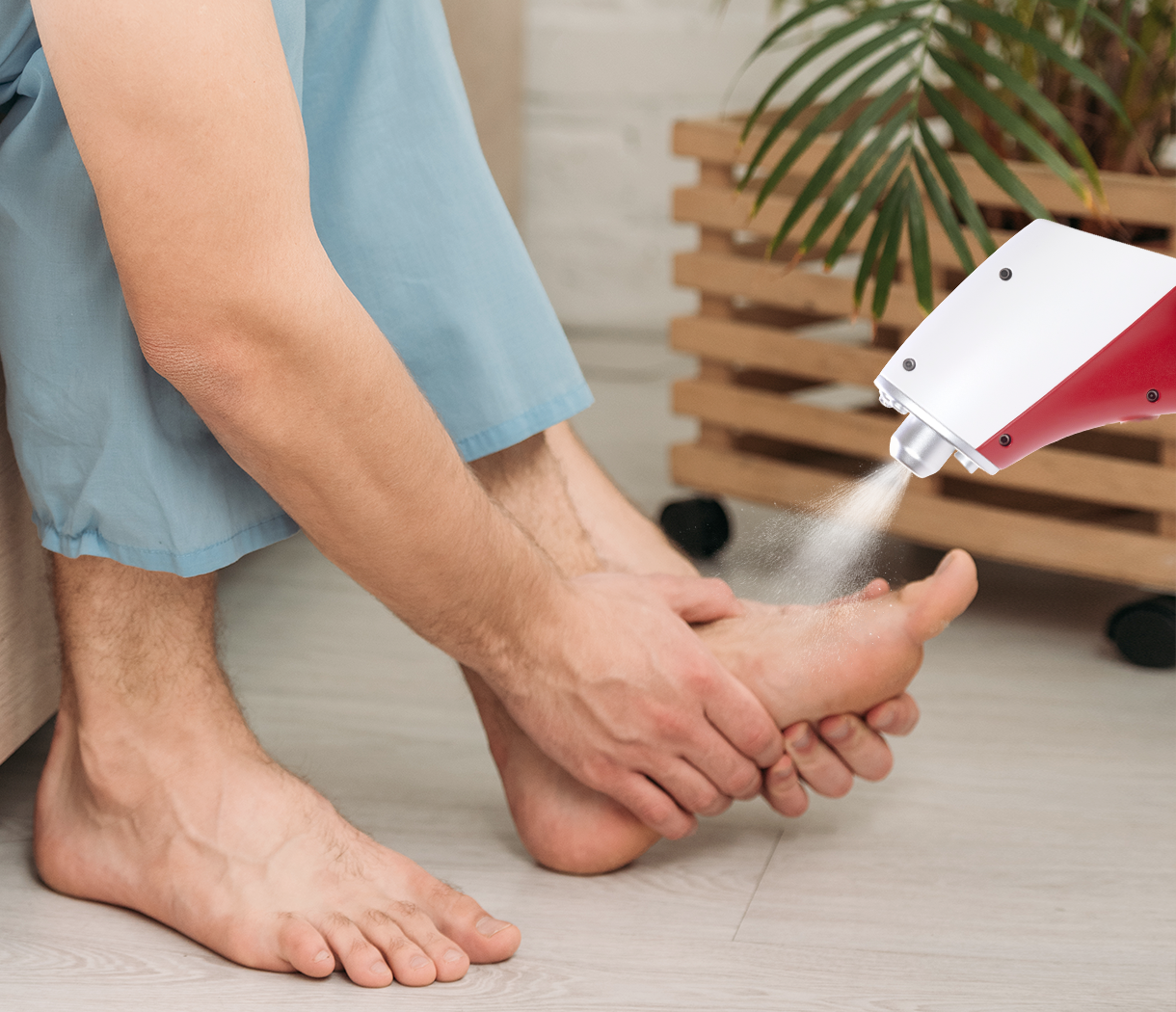
Instant CO₂ cooling represents a sophisticated form of targeted cryotherapy that utilizes carbon dioxide gas to achieve rapid, controlled tissue cooling. This technology operates by delivering CO₂ at extremely low temperatures, typically reaching -78°C (-108°F), directly to the affected tissue surface. The therapeutic mechanism involves precise temperature control that induces immediate physiological responses beneficial for acute injury management. The rapid cooling effect triggers vasoconstriction, reduces metabolic activity, and initiates cellular protective mechanisms that collectively minimize tissue damage and promote healing while providing immediate pain relief.
Overview of Cryotherapy for Acute Injury Management
Cryothérapie has been a cornerstone of acute injury management for decades, based on well-established physiological principles that promote healing and reduce injury-related complications. Traditional cryotherapy modalities include ice packs, cold water immersion, and frozen gel applications, each with distinct advantages and limitations. The anti-inflammatory, anti-analgesic, and anti-oxidant effects of this therapy have been confirmed by recent studies highlighting the underlying physiological responses. The therapeutic benefits of cryotherapy encompass pain reduction, inflammation control, metabolic rate decrease, and enhanced tissue preservation during the critical acute injury phase.
Why CO₂ Cooling Stands Out: Key Advantages
CO₂ cooling distinguishes itself from conventional cryotherapy through several unique characteristics that enhance its therapeutic effectiveness. The primary advantage lies in its ability to achieve rapid, uniform cooling with precise temperature control, eliminating the inconsistencies often associated with traditional ice applications. The cooling effect induces vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels), which reduces swelling, inflammation, and pain. In addition, the thermal shock response from rapid temperature change boosts circulation and stimulates cellular recovery. The portability and immediate availability of CO₂ cooling systems make them particularly valuable in emergency and sports medicine settings where rapid intervention is essential.
The Science Behind Instant CO₂ Cooling
Understanding the scientific foundation of CO₂ cooling requires examination of its complex physiological mechanisms and cellular interactions. The therapeutic efficacy of this modality stems from its ability to rapidly alter tissue temperature and trigger beneficial physiological responses that collectively promote healing and reduce injury severity.
Mechanism of Action: How CO₂ Cooling Works
The mechanism of CO₂ cooling involves the rapid expansion of compressed carbon dioxide gas, which creates an endothermic reaction that dramatically lowers surface temperature. When CO₂ is released from its compressed state, it undergoes sublimation, transitioning directly from solid to gas phase while absorbing significant amounts of thermal energy from surrounding tissues. This process can reduce tissue temperature to -78°C within seconds, creating a controlled thermal gradient that penetrates into deeper tissue layers. The rapid cooling initiates immediate physiological responses including vasoconstriction, reduced nerve conduction velocity, and decreased cellular metabolic activity, all of which contribute to therapeutic benefit.
Physiological Effects: Vasoconstriction and Inflammation Reduction
The primary physiological effect of CO₂ cooling is the induction of immediate vasoconstriction, which serves multiple therapeutic purposes in acute injury management. The physiologic effects of cold application include immediate vasoconstriction with reflexive vasodilation, decreased local metabolism and enzymatic activity, and decreased oxygen demand. This vascular response reduces blood flow to the injured area, limiting the extravasation of inflammatory mediators and reducing tissue edema. The vasoconstriction also helps control hemorrhage in acute traumatic injuries, preventing the formation of large hematomas that can complicate healing. Additionally, the reduced blood flow decreases the delivery of inflammatory cells and mediators to the injury site, effectively dampening the inflammatory response.
Cellular Impact: Slowing Metabolism and Reducing Tissue Damage
At the cellular level, CO₂ cooling produces profound metabolic effects that protect tissues from secondary injury. Speculated mechanisms enhancing fatigue recovery by cryotherapy include reduced inflammation by cold-induced vasoconstriction and reduction of metabolic enzymatic activity, leading to limited secondary hypoxic damage to uninjured cells. The rapid temperature reduction decreases cellular oxygen demand by slowing metabolic processes, effectively creating a protective metabolic state that prevents cellular death in compromised tissues. This metabolic suppression is particularly important in preventing the cascade of secondary injury that often occurs following the initial trauma, preserving tissue viability and promoting better healing outcomes.
Clinical Applications of Instant CO₂ Cooling
The versatility of instant CO₂ cooling makes it applicable across a broad spectrum of acute injury scenarios, from minor sports injuries to more complex trauma cases. Understanding the specific applications and optimal usage protocols is essential for maximizing therapeutic benefit and ensuring patient safety.
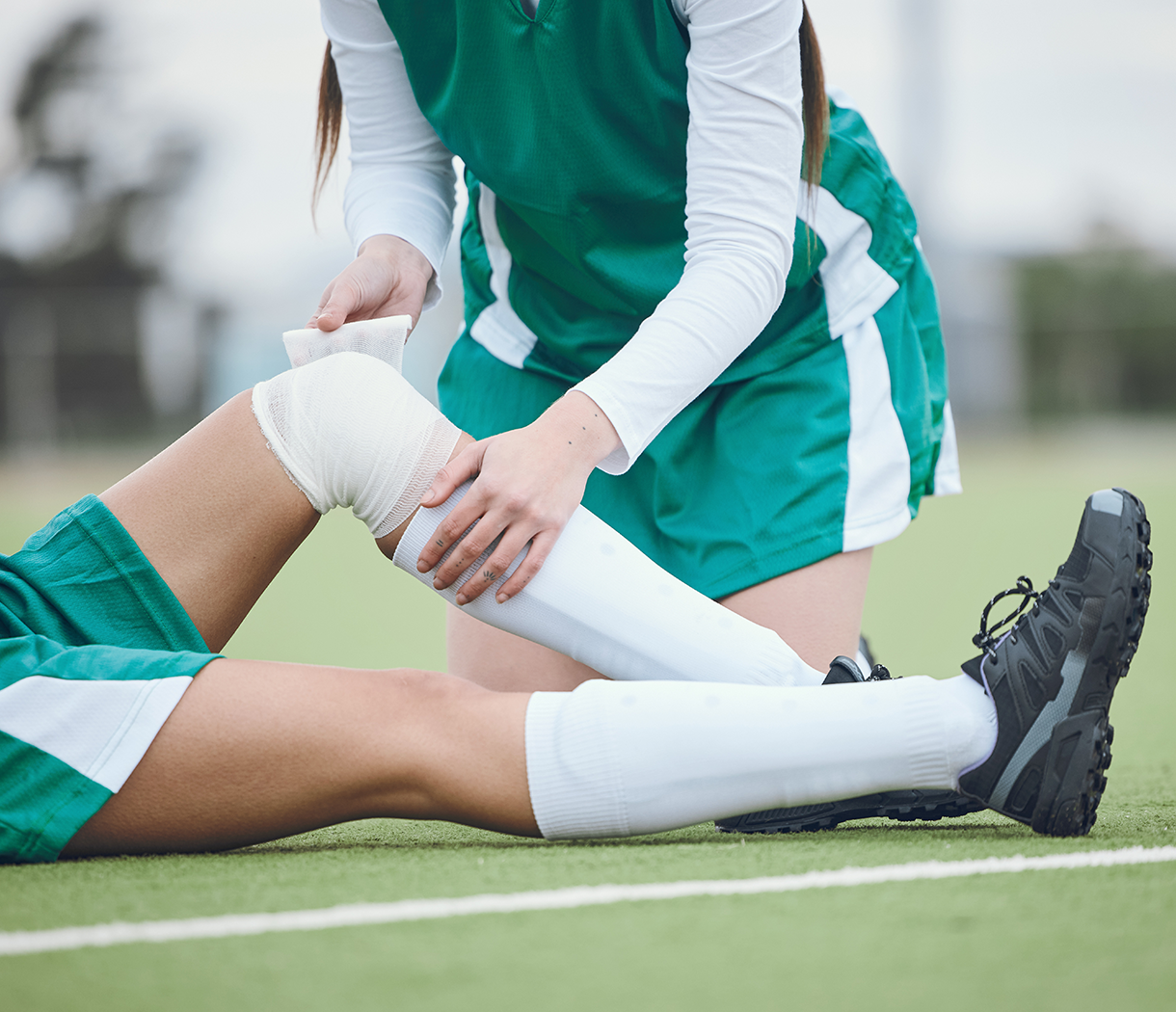
Managing Sprains and Strains
Sprains and strains represent the most common acute musculoskeletal injuries, often involving ligamentous or muscular tissue damage with associated inflammation and pain. CO₂ cooling provides immediate relief by reducing tissue temperature and limiting the inflammatory response that typically exacerbates these injuries. The rapid cooling effect helps control swelling and hemorrhage within the injured tissue, preventing the formation of excessive scar tissue that can impair function. Treatment typically involves 10-15 second applications directly to the affected area, repeated at appropriate intervals to maintain therapeutic benefit without causing tissue damage. The precision of CO₂ cooling allows for targeted treatment of specific anatomical structures while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues.
Use in Sports-Related Injuries and Trauma Recovery
Sports medicine has embraced CO₂ cooling as a valuable tool for managing acute athletic injuries and facilitating rapid return to activity. The immediate availability and portability of CO₂ cooling systems make them ideal for sideline treatment of acute injuries during sporting events. CO₂ cryotherapy rapidly cools tissue, lowering cellular metabolism and reducing inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins and cytokines. This helps prevent secondary tissue damage. The technology is particularly effective for treating acute contusions, muscle strains, and minor joint injuries that commonly occur in athletic activities. The rapid cooling effect can provide immediate pain relief, allowing for proper assessment of injury severity and informed decisions regarding continued participation or need for further medical evaluation.
Alleviating Acute Back and Neck Pain
Acute back and neck pain often result from muscle spasms, inflammation, or minor traumatic injuries that can be effectively managed with targeted CO₂ cooling therapy. The application of CO₂ cooling to affected spinal regions can provide immediate pain relief by reducing nerve conduction velocity and interrupting pain signal transmission. Cold decreases muscle spindle fiber activity and slows nerve conduction velocity; therefore, it is often used for pain management. The cooling effect also helps reduce muscle spasm and inflammation associated with acute spinal injuries, allowing for improved mobility and function. Treatment protocols typically involve systematic cooling of affected muscle groups and trigger points, providing comprehensive pain relief and functional improvement.
Supporting Post-Surgical and Post-Injection Recovery
CO₂ cooling has found valuable applications in post-surgical and post-injection recovery protocols, where controlling inflammation and pain is crucial for optimal outcomes. Following surgical procedures, immediate cooling can help reduce post-operative swelling and pain, potentially decreasing the need for systemic analgesics. The controlled cooling effect helps manage the inflammatory response associated with surgical trauma while preserving tissue viability and promoting healing. In post-injection scenarios, CO₂ cooling can effectively manage injection site reactions, reducing pain and inflammation while preventing complications. The precise temperature control and brief application duration make CO₂ cooling particularly suitable for these sensitive clinical situations where traditional ice therapy might be too aggressive or impractical.
Benefits in Reducing Swelling and Bruising
One of the most visible benefits of CO₂ cooling is its effectiveness in reducing swelling and bruising associated with acute injuries. The rapid vasoconstriction induced by cold therapy helps limit the extravasation of blood and inflammatory fluids into surrounding tissues, preventing the formation of extensive hematomas and edema. Based on the available evidence, cryotherapy seems to be effective in decreasing pain. The controlled cooling effect helps maintain tissue integrity while promoting the reabsorption of accumulated fluids, leading to faster resolution of swelling and improved cosmetic outcomes. This benefit is particularly important in facial injuries, where swelling and bruising can have significant functional and aesthetic implications. The precise application of CO₂ cooling allows for targeted treatment of specific areas while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues.
Advantages of Instant CO₂ Cooling over Traditional Methods
The superiority of instant CO₂ cooling over traditional cryotherapy methods lies in its technological sophistication and clinical versatility. These advantages translate into improved patient outcomes, enhanced treatment precision, and greater clinical practicality across various healthcare settings.
Rapid Temperature Reduction and Deep Tissue Penetration
The main advantage of CO₂ cooling is its ability to quickly and precisely lower temperatures, reaching deeper tissue layers. Unlike traditional ice therapy, which can take several minutes to cool, CO₂ cooling drops surface temperature to -78°C within seconds. This rapid cooling creates a thermal gradient that reaches deeper tissues, providing effective treatment for areas often missed by conventional methods. The cryotherapy effect depends on factors like method, duration, ice temperature, and subcutaneous fat depth. The controlled delivery system ensures consistent temperature and penetration depth, removing the variability of traditional ice treatments.
Portability and Convenience for On-Site Treatment
The portability of CO₂ cooling systems is a major advantage in emergency and sports medicine. Unlike traditional ice therapy, which requires preparation and storage, CO₂ systems are ready for immediate use. Their compact, lightweight design makes them ideal for athletic trainers, emergency responders, and healthcare providers. This immediate availability optimizes the golden hour for acute injury management, improving patient outcomes through timely intervention. The ease of use also boosts compliance, encouraging consistent application of treatment.
Reduced Risk of Frostbite and Skin Damage
Traditional ice therapy carries inherent risks of frostbite and skin damage, particularly with prolonged application or in patients with compromised circulation. CO₂ cooling systems incorporate sophisticated safety features that minimize these risks through precise temperature control and automatic shut-off mechanisms. The controlled delivery system ensures that therapeutic temperatures are maintained without exceeding safe limits, reducing the potential for tissue damage. Additionally, the brief application duration typical of CO₂ cooling protocols (10-15 seconds) minimizes exposure time while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. This safety profile makes CO₂ cooling suitable for a broader range of patients, including those with conditions that might contraindicate traditional ice therapy.
Enhanced Patient Comfort and Compliance
Patient comfort and compliance are significantly improved with CO₂ cooling compared to traditional methods. The brief, controlled application eliminates the prolonged discomfort associated with ice therapy, making the treatment more tolerable for patients. The precise temperature control prevents the extreme cold sensation that often causes patient discomfort and treatment discontinuation with traditional ice applications. High patient satisfaction and a favorable safety profile suggest its potential for clinical use. The improved patient experience promotes better compliance with treatment protocols, ultimately leading to better clinical outcomes. The professional appearance and sophisticated technology of CO₂ cooling systems also enhance patient confidence in the treatment approach, contributing to overall satisfaction with care.
Considérations de sécurité et contre-indications
While CO₂ cooling offers significant therapeutic benefits, proper safety protocols and awareness of contraindications are essential for safe and effective clinical application. Understanding these considerations ensures optimal patient outcomes while minimizing potential risks and complications.
Identifying Patients Unsuitable for CO₂ Cryotherapy
Certain patient populations require special consideration or may be unsuitable for CO₂ cooling therapy due to underlying medical conditions or physiological factors. Patients with severe peripheral vascular disease, including those with advanced diabetes or atherosclerotic conditions, may have compromised circulation that increases the risk of cold-induced tissue damage. Individuals with cold hypersensitivity disorders, including cryoglobulinemia, cold urticaria, or Raynaud’s phenomenon, may experience severe adverse reactions to cold therapy. Additionally, patients with significant cognitive impairment who cannot provide reliable feedback about temperature sensation and comfort levels may be at increased risk for cold-related injuries. Healthcare providers must carefully assess each patient’s medical history and current condition before implementing CO₂ cooling therapy.
Proper Usage Guidelines and Treatment Duration
Proper usage of CO₂ cooling systems requires adherence to established protocols that balance therapeutic efficacy with patient safety. Treatment duration should typically be limited to 10-15 seconds per application site to prevent tissue damage while maintaining therapeutic benefit. Multiple applications may be performed with appropriate intervals between treatments to allow tissue temperature normalization. The treatment area should be properly prepared, with clean, dry skin and removal of any topical medications or substances that might interfere with cooling or increase skin sensitivity. Healthcare providers should maintain constant visual monitoring during treatment and be prepared to discontinue therapy immediately if adverse reactions occur. Patient positioning should ensure comfort and accessibility while preventing accidental contact with non-target areas.
Avoiding Complications: Skin Protection and Monitoring
Effective skin protection and monitoring protocols are essential for preventing complications during CO₂ cooling therapy. The treatment area should be thoroughly inspected before and after each application to identify any signs of skin damage, irritation, or abnormal response. Patients should be educated about normal sensations during treatment and instructed to immediately report any unusual pain, burning, or discomfort. Healthcare providers should maintain continuous observation during treatment, watching for signs of excessive vasoconstriction, skin color changes, or patient distress. Post-treatment monitoring should include assessment of skin integrity, sensation, and any delayed reactions. Documentation of treatment parameters, patient response, and any adverse events is crucial for maintaining safety records and informing future treatment decisions.
Contraindications: Vascular Conditions and Cold Sensitivity
Specific contraindications for CO₂ cooling therapy include conditions that affect vascular function or increase cold sensitivity. Absolute contraindications are severe peripheral vascular disease, active vascular compromise, and cold hypersensitivity disorders. Relative contraindications need careful consideration. These may include mild vascular insufficiency, recent surgery in the treatment area, and certain medications affecting vascular function. Patients with compromised sensation, such as those with diabetic neuropathy or other nerve disorders, may struggle to provide adequate feedback on temperature sensation. Healthcare providers must evaluate each patient’s vascular status and cold sensitivity before using CO₂ cooling. This ensures a balance between potential benefits and risks.
Common Side Effects and Risk Management of CO₂ Cryotherapy
While CO₂ cooling is generally well-tolerated, healthcare providers should be aware of potential side effects and implement appropriate risk management strategies. Common side effects include temporary skin redness, mild discomfort during application, and transient numbness in the treated area. Cryotherapy may safely be used in musculoskeletal injuries and dysfunctions. It is well tolerated by patients. More serious but rare complications may include frostbite, skin damage, or exacerbation of underlying vascular conditions. Risk management strategies include proper patient selection, adherence to treatment protocols, continuous monitoring during therapy, and immediate intervention if adverse reactions occur. Healthcare providers should maintain current knowledge of safety protocols and be prepared to manage complications effectively. Patient education about potential side effects and appropriate post-treatment care is essential for ensuring safe and effective therapy outcomes.
Evidence-Based Benefits and Clinical Studies
The clinical efficacy of CO₂ cooling is supported by a growing body of research evidence that demonstrates its therapeutic benefits across various acute injury scenarios. This scientific foundation provides the basis for evidence-based clinical decision-making and treatment protocol development.
Summary of Key Research Findings on CO₂ Cooling Efficacy
Recent research has provided compelling evidence for the therapeutic efficacy of CO₂ cooling in acute injury management. Studies indicate that cryotherapy with carbon dioxide hydrate enhances immediate recovery of muscle function from neuromuscular fatigue and improves muscle blood circulation. Clinical trials demonstrate significant improvements in pain reduction, swelling control, and functional recovery when CO₂ cooling is implemented as part of acute injury protocols. Research findings consistently show that CO₂ cooling provides superior temperature control and tissue penetration compared to traditional ice therapy, leading to enhanced therapeutic outcomes. The studies also demonstrate the safety profile of CO₂ cooling, with minimal adverse events reported when proper protocols are followed.
Case Studies in Acute Injury Management
Clinical case studies have provided valuable insights into the practical application and effectiveness of CO₂ cooling in real-world acute injury scenarios. These studies document significant improvements in patient outcomes when CO₂ cooling is implemented as part of comprehensive injury management protocols. Case reports have demonstrated particularly impressive results in sports-related injuries, where rapid cooling has facilitated earlier return to activity and reduced the risk of chronic complications. The case studies also highlight the importance of proper patient selection, treatment timing, and adherence to established protocols for achieving optimal outcomes. These real-world examples provide valuable guidance for healthcare providers considering the implementation of CO₂ cooling in their clinical practice.
Comparison of Recovery Times with Other Cooling Modalities
Comparative studies have consistently shown faster recovery times with CO₂ cooling compared to traditional cooling methods. Most studies using cryotherapy for post-exercise recovery highlight its effectiveness in reducing inflammation by lowering local metabolism and inducing vasoconstriction. Research indicates that patients treated with CO₂ cooling experience quicker resolution of swelling, reduced pain duration, and an earlier return to normal function than those treated with conventional ice therapy. The studies also report higher patient satisfaction and better compliance with CO₂ cooling protocols compared to traditional methods. These findings support the adoption of CO₂ cooling as a preferred option for acute injury management in clinical settings.
Integrating Instant CO₂ Cooling into Acute Injury Protocols
The successful integration of CO₂ cooling into existing acute injury protocols requires careful consideration of clinical workflows, staff training, and interdisciplinary collaboration. This integration process ensures that the benefits of CO₂ cooling are maximized while maintaining efficient and effective patient care.
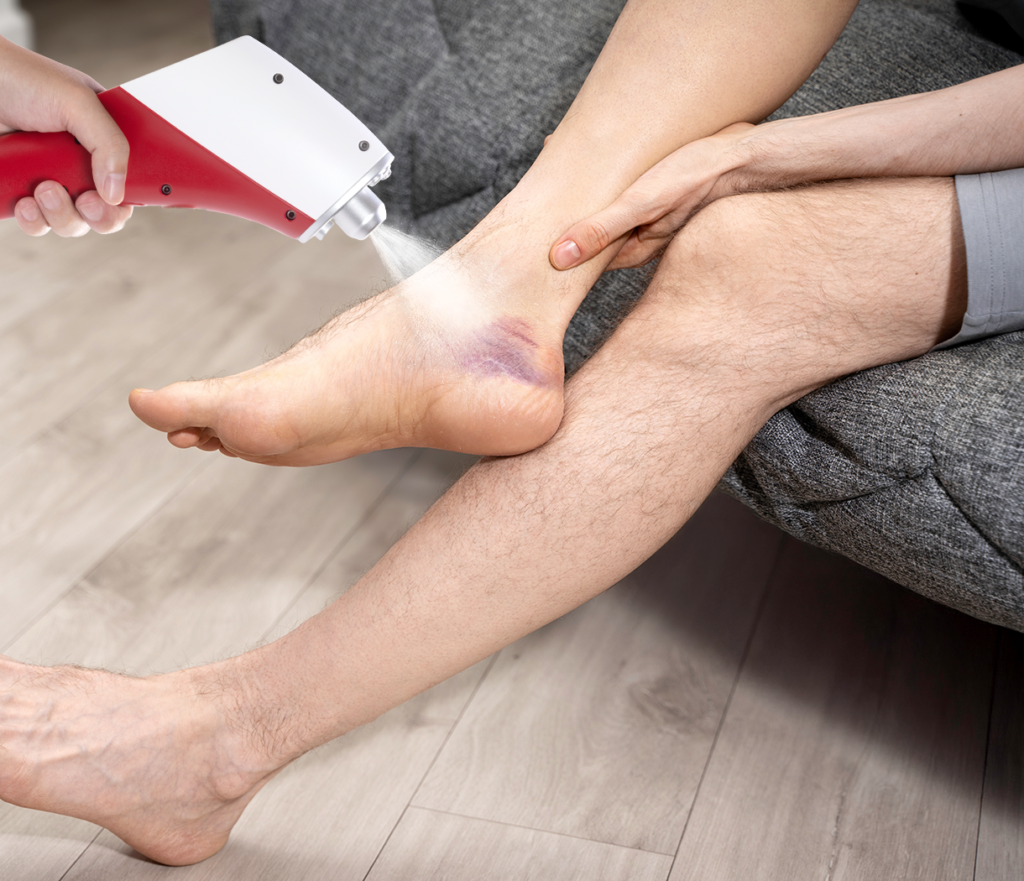
Role in Emergency and Sports Medicine
CO₂ cooling plays a crucial role in emergency and sports medicine, where rapid intervention is key for optimal outcomes. Emergency departments now use CO₂ cooling as a first-line treatment for certain acute injuries. This provides immediate pain relief and controls inflammation. In sports medicine, CO₂ cooling is essential for managing sideline injuries. It allows for quick assessment and treatment during competitive events. The portability and immediate availability of CO₂ cooling systems make them ideal for dynamic environments where traditional methods may not be practical. Healthcare providers report better patient outcomes and improved treatment efficiency with CO₂ cooling.
Combining CO₂ Cooling with Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Integrating CO₂ cooling with physical therapy and rehabilitation has shown promising results in accelerating recovery. It improves functional outcomes as well. Physical therapists use CO₂ cooling before therapeutic exercises to reduce pain and inflammation, which may limit participation. This cooling effect enhances the effectiveness of subsequent treatments by improving patient comfort and reducing muscle guarding. CO₂ cooling is also used post-exercise to manage inflammation and soreness from progressive rehabilitation. This integrated approach yields better results than traditional rehabilitation methods alone.
Best Practices for Clinicians and Patients
Successful implementation of CO₂ cooling requires adherence to established best practices that ensure both safety and efficacy. Clinicians should receive comprehensive training in CO₂ cooling techniques, safety protocols, and contraindications before implementing this therapy in clinical practice. Patient education is equally important, including instruction on expected sensations during treatment, potential side effects, and post-treatment care. Best practices include proper patient positioning, skin preparation, treatment duration monitoring, and post-treatment assessment. Healthcare providers should maintain current knowledge of evolving protocols and safety guidelines through continuing education and professional development. Regular equipment maintenance and safety checks are essential for ensuring optimal performance and patient safety.
Foire aux questions (FAQ)
A typical CO₂ cooling treatment lasts 10-15 seconds per application site. Multiple applications may be performed with appropriate intervals between treatments to allow tissue temperature normalization.
CO₂ cooling is generally safe for most patients, but certain conditions require special consideration. Patients with severe peripheral vascular disease, cold hypersensitivity disorders, or compromised sensation may not be suitable candidates for this therapy.
CO₂ cooling offers several advantages over traditional ice therapy, including rapid temperature reduction, precise temperature control, improved portability, and reduced risk of frostbite. The treatment duration is also significantly shorter while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.
Yes, CO₂ cooling can be used immediately after injury and is most effective when applied during the acute phase. Cryotherapy may be recommended in the first 6 hours following an injury to reduce pain and possibly reduce hematoma formation.
Common side effects include temporary skin redness, mild discomfort during application, and transient numbness. Serious complications are rare when proper protocols are followed and appropriate patients are selected.
CO₂ cooling can be applied multiple times per day as needed, with appropriate intervals between applications to allow tissue temperature normalization. The specific frequency depends on the injury type and patient response.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Instant CO₂ Cooling in Fast, Effective Injury Recovery
Instant CO₂ cooling is a major advancement in acute injury management, offering faster and more effective relief than traditional methods. Its rapid, controlled cooling promotes vasoconstriction, reduces inflammation, and slows metabolism, which helps minimize pain and swelling immediately after injury. Scientific studies consistently show that CO₂ cooling improves recovery times and functional outcomes, especially in emergency and sports medicine settings where quick intervention is critical. With proper safety protocols, CO₂ cooling is suitable for diverse patients and reduces risks compared to other cryotherapy options. Integrating this technology into acute injury care enhances clinical efficiency and patient satisfaction. As healthcare evolves toward precise, evidence-based treatments, instant CO₂ cooling exemplifies innovation that improves patient outcomes. It is now an essential, reliable tool for accelerating recovery and improving quality of life for those with acute injuries.



