Introduction
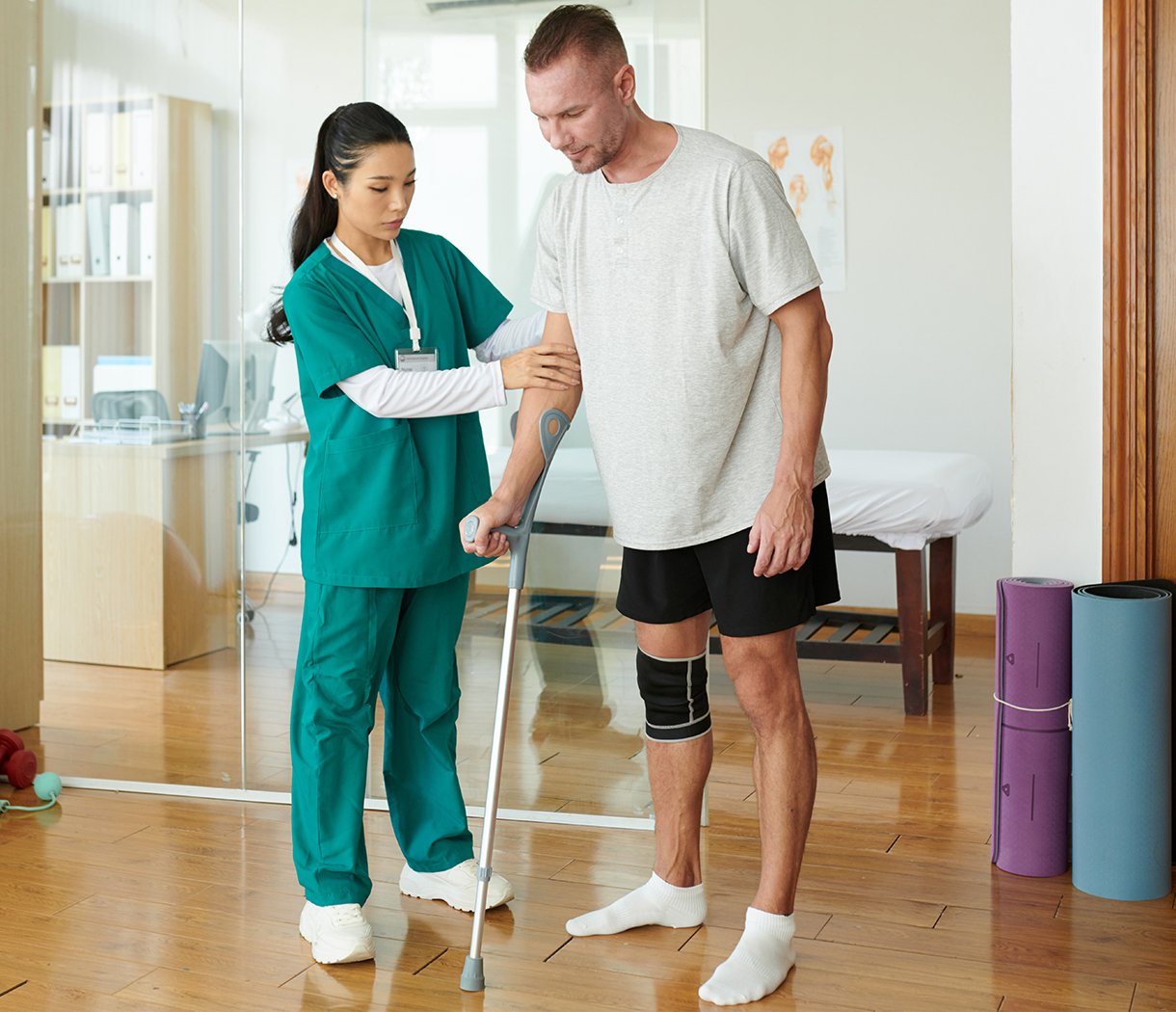
Stroke, or cerebrovascular accident (CVA), remains one of the leading causes of long-term disability worldwide. Survivors often face a range of complications, including muscle weakness, spasticity, chronic pain, and impaired mobility. Traditional rehabilitation strategies, such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and pharmacological interventions, aim to restore function and prevent further complications. However, many patients experience persistent symptoms despite intensive therapy. In recent years, CO₂ Cryotherapy has emerged as a promising non-invasive adjunct therapy in stroke rehabilitation. By delivering controlled cold carbon dioxide gas to affected tissues, this technique promotes blood flow, reduces inflammation, alleviates pain, and enhances muscle function. This article explores the mechanisms, benefits, protocols, and practical considerations of CO₂ Cryotherapy in post-stroke rehabilitation, providing evidence-based guidance for clinicians and patients alike.
1. Understanding Stroke and Its Effects
1.1 What Happens During a Stroke?
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving neural tissue of oxygen and nutrients. The two main types are ischemic stroke, caused by arterial blockage, and hemorrhagic stroke, resulting from a ruptured blood vessel. Neuronal death and disruption of neural networks can lead to hemiparesis, sensory deficits, and impaired coordination. The extent of neurological damage depends on the location and duration of the ischemic event.
Beyond immediate neurological deficits, stroke often triggers secondary complications such as spasticity, contractures, and peripheral circulatory problems. These changes affect skeletal muscles, connective tissue, and local blood flow, complicating rehabilitation efforts. Understanding the underlying pathophysiology is crucial when selecting therapies that target both neural and musculoskeletal recovery.
1.2 Common Post-Stroke Symptoms
Post-stroke symptoms are diverse and may include hemiplegia or hemiparesis, increased muscle tone (spasticity), joint stiffness, and chronic pain. Patients frequently report impaired range of motion, difficulty with gait, and functional limitations in daily activities. Sensory deficits, including numbness or abnormal sensations, can further impede rehabilitation.
Circulatory problems are also common, particularly in extremities affected by paresis. Poor blood flow can exacerbate tissue stiffness, delay muscle recovery, and increase the risk of secondary injuries. Addressing both neurological and peripheral tissue changes is essential for comprehensive rehabilitation, which is where CO₂ Cryotherapy may offer additional benefits.
2. What is CO₂ Cryotherapy?
2.1 Definition and Mechanism
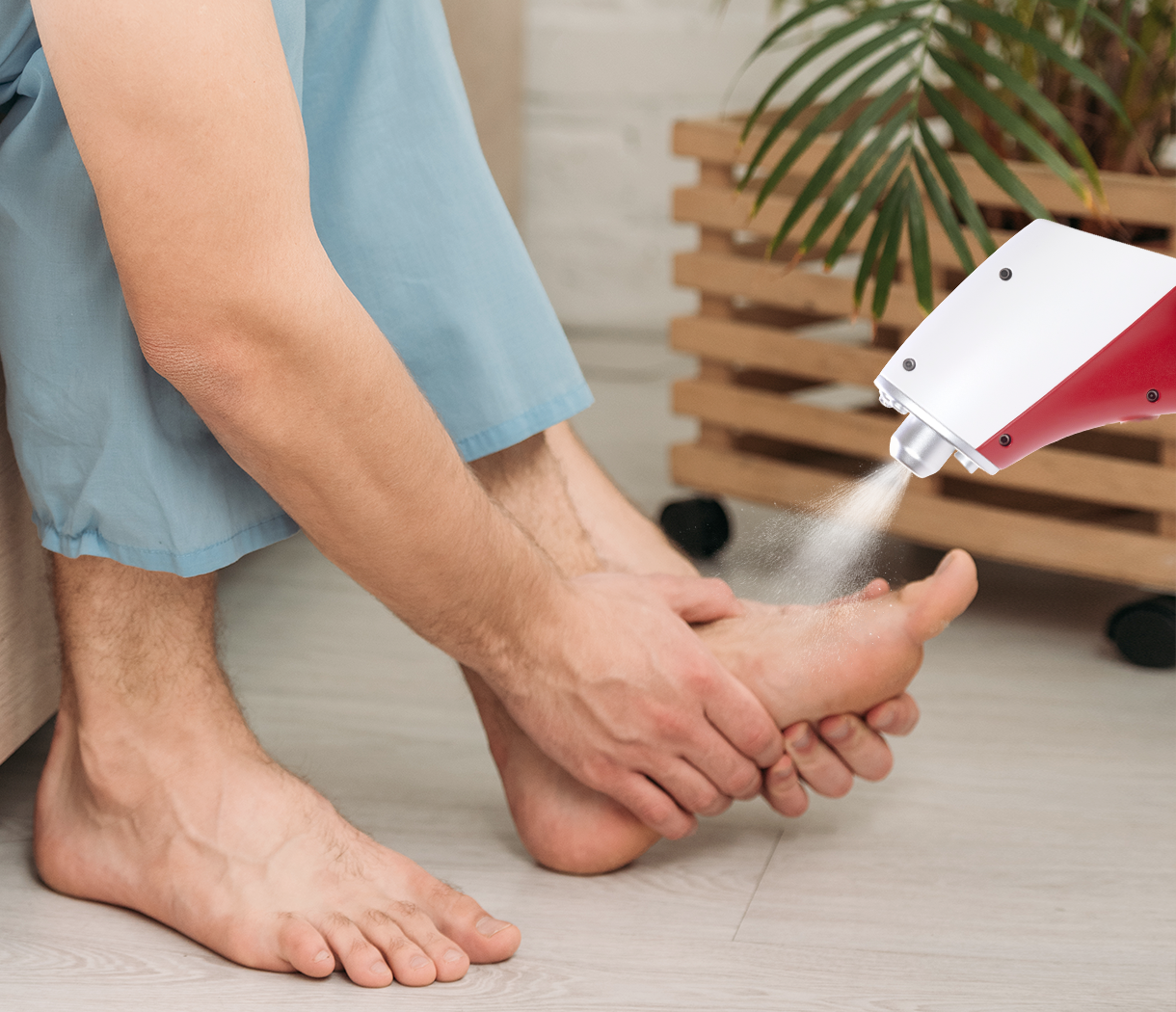
CO₂ Cryotherapy is a therapeutic modality that utilizes carbon dioxide gas at subzero temperatures to deliver controlled cold exposure to localized tissues. Unlike systemic cooling or ice packs, this technique provides precise, non-invasive cooling without damaging superficial skin layers. The cold gas induces vasoconstriction followed by reactive vasodilation, improving microcirculation and oxygen delivery to tissues.
At a cellular level, CO₂ Cryotherapy reduces inflammatory mediators, modulates nociceptor activity, and promotes metabolic recovery. In the context of stroke rehabilitation, these mechanisms help decrease muscle spasticity, reduce pain, and improve soft tissue flexibility. By targeting peripheral tissues, CO₂ Cryotherapy complements neural rehabilitation strategies that aim to restore motor function and coordination.
2.2 How CO₂ Cryotherapy Supports Stroke Recovery
CO₂ Cryotherapy addresses the peripheral components of post-stroke disability. By improving microvascular perfusion, it enhances oxygen and nutrient delivery to muscles affected by spasticity or paresis. The therapy also reduces edema and inflammation, which can otherwise hinder muscle elasticity and joint mobility.
Moreover, localized cooling has an analgesic effect, decreasing pain signaling from overactive nociceptors in stiff or inflamed muscles. When combined with neurorehabilitation, CO₂ Cryotherapy facilitates more effective physical therapy sessions by allowing patients to move affected limbs with less discomfort. This integration can accelerate functional recovery and improve quality of life for stroke survivors.
3. Benefits of CO₂ Cryotherapy for Stroke Rehabilitation
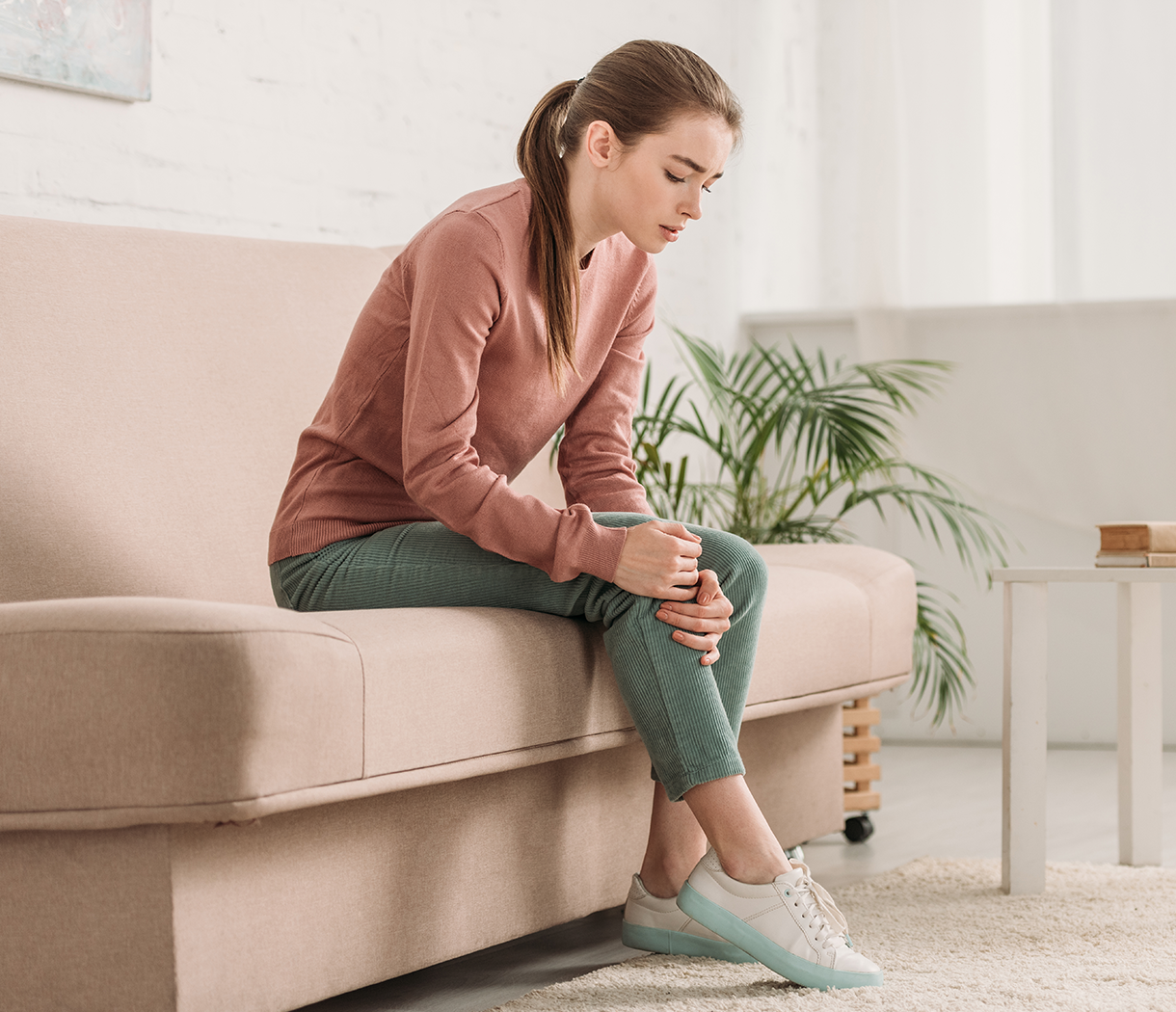
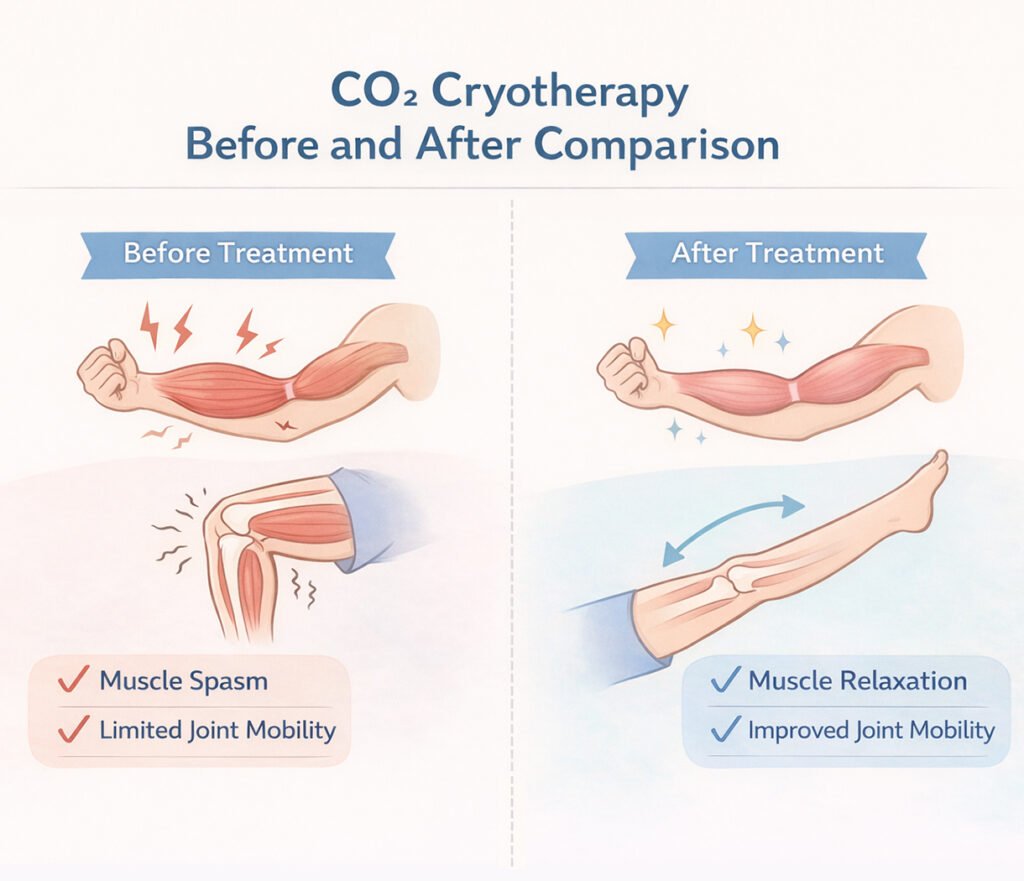
3.1 Pain Relief and Muscle Relaxation
Post-stroke spasticity often causes significant discomfort, limiting rehabilitation efforts. CO₂ Cryothérapie reduces pain by temporarily slowing nerve conduction and desensitizing nociceptors. The cold stimulus also relaxes hypertonic muscles, decreasing tension and stiffness.
Clinical observations indicate that patients experience immediate relief in targeted areas, which can enhance participation in physiotherapy. By providing a non-drug pain management option, CO₂ Cryotherapy reduces reliance on analgesics, minimizing side effects such as sedation or gastrointestinal issues. Over time, consistent treatment may contribute to improved overall comfort and functional engagement.
3.2 Improved Circulation and Tissue Oxygenation
Cold application triggers an initial vasoconstriction followed by reactive hyperemia, enhancing blood flow to treated tissues. Improved circulation delivers oxygen and nutrients essential for muscle repair, reduces metabolic waste accumulation, and supports tissue recovery.
For stroke patients with compromised limb perfusion, enhanced microcirculation can mitigate complications such as edema and tissue hypoxia. Better oxygenation also aids in maintaining muscle elasticity and preventing secondary contractures, creating favorable conditions for effective neurorehabilitation.
3.3 Enhancing Mobility and Range of Motion
Reduced pain and inflammation from CO₂ Cryotherapy contribute directly to increased range of motion. Muscles affected by spasticity can be gently stretched during or after treatment, enabling more effective physical therapy.
By facilitating movement without discomfort, patients can perform functional exercises with greater compliance. Over multiple sessions, CO₂ Cryotherapy helps maintain joint flexibility, prevent contractures, and support gradual restoration of motor control. This synergistic effect accelerates rehabilitation outcomes and promotes independence in daily activities.
3.4 Non-Invasive and Safe
CO₂ Cryotherapy is non-invasive, requires no anesthesia, and avoids systemic drug exposure. The therapy is generally well-tolerated, with minimal side effects such as transient redness or mild tingling at the treatment site.
Its safety profile allows for repeated use over weeks or months, making it suitable for both acute and chronic stages of stroke recovery. This low-risk modality offers a complementary approach alongside conventional therapies, ensuring patients receive comprehensive care without additional medical complications.
4. Treatment Protocols for Stroke Patients
4.1 Frequency and Duration
Typical CO₂ Cryotherapy sessions for post-stroke rehabilitation range from 10 to 20 minutes, administered 2–3 times per week depending on patient tolerance and recovery stage. Early intervention may focus on mild, localized applications to prevent overstimulation of sensitive tissues.
Therapists monitor patient responses to adjust treatment duration and intensity. Consistency is key: multiple sessions over several weeks yield cumulative benefits in pain reduction, muscle relaxation, and joint mobility. Individualized protocols ensure both safety and maximum therapeutic effect.
4.2 Combining with Physical Therapy
CO₂ Cryotherapy works best when integrated with traditional rehabilitation strategies. Following a session, patients may engage in stretching, gait training, or functional exercises to capitalize on reduced spasticity and increased flexibility.
The therapy prepares muscles and joints for movement, enhancing the efficacy of physical therapy. By combining peripheral tissue treatment with neurorehabilitation, patients can achieve more meaningful gains in strength, coordination, and independence than with either approach alone.
4.3 Monitoring Progress
Monitoring treatment outcomes involves assessing pain levels, muscle tone, range of motion, and functional ability. Therapists often use scales such as the Modified Ashworth Scale for spasticity and the Fugl-Meyer Assessment for motor recovery.
Regular evaluation helps clinicians determine whether therapy intensity or frequency requires adjustment. Over time, objective improvements in limb mobility and patient-reported reductions in discomfort indicate successful integration of CO₂ Cryotherapy into the rehabilitation plan.
5. Who Can Benefit Most?
5.1 Ideal Candidates
Patients experiencing post-stroke spasticity, limb stiffness, and chronic pain are ideal candidates. Those in the subacute or chronic phases of recovery, who have completed initial stabilization, often benefit the most from peripheral tissue-focused interventions.
Additionally, patients who have limited tolerance to pharmacological interventions or prefer non-drug approaches may find CO₂ Cryotherapy particularly appealing. The therapy complements ongoing rehabilitation while minimizing additional systemic risks.
5.2 When to Consider CO₂ Cryotherapy
CO₂ Cryotherapy is most effective when used as part of a comprehensive stroke rehabilitation program. Early incorporation can help mitigate the development of contractures, reduce secondary complications, and prepare tissues for physical therapy.
For chronic cases, the therapy may still provide meaningful relief from persistent spasticity and pain, allowing patients to engage more fully in functional exercises and daily activities. Consultation with a rehabilitation physician or therapist ensures appropriate timing and individualized application.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: Is CO₂ Cryotherapy safe for all stroke patients?
Generally, yes, but patients with severe sensory deficits or vascular conditions should be evaluated before treatment.
Q2: How quickly can patients expect improvement?
Some patients notice immediate relief in muscle tension, but functional gains typically accumulate over weeks of consistent therapy.
Q3: Can CO₂ Cryotherapy replace standard physical therapy?
No. It is an adjunct therapy that enhances the effectiveness of conventional rehabilitation exercises.
Q4: Are there any side effects?
Side effects are minimal, usually limited to transient redness, tingling, or mild discomfort at the treated area.
Q5: How often should therapy be administered?
Most protocols recommend 2–3 sessions per week, adjusted based on patient response and recovery phase.
Conclusion
CO₂ Cryotherapy offers a non-invasive, safe, and effective adjunct to traditional stroke rehabilitation. By reducing pain, alleviating spasticity, and improving circulation, it enhances patients’ ability to participate in physical therapy and regain functional independence. Integrating CO₂ Cryotherapy into a comprehensive rehabilitation program can accelerate recovery, improve quality of life, and provide a drug-free option for managing post-stroke complications.
Références
Lyons, R., & King, C. (2020). Cryotherapy in Stroke Rehabilitation: Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, 17(1), 101.
https://jneuroengrehab.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12984-020-00756-4
Côté, J. N., & Mathieu, P. A. (2018). Peripheral Cold Therapy and Neuromuscular Recovery Post-Stroke. Frontiers in Neurology, 9, 234.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2018.00234/full
Hesse, S., Werner, C., & Jahnke, M. (2017). Rehabilitation of Upper Limb Spasticity After Stroke. NeuroRehabilitation, 41(2), 219–228.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28458720/
Petrov, R., & Todorova, T. (2019). Cold Gas Therapy for Muscle Recovery and Pain Relief. Clinical Rehabilitation, 33(5), 1020–1030.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30607288/
Heuschmann, P. U., et al. (2016). Post-Stroke Care: Long-Term Rehabilitation and Recovery. Lancet Neurology, 15(10), 1014–1025.



