Repetitive Strain Syndrome (RSS) is more than a nuisance—it’s a debilitating condition that can steal productivity, cause chronic pain, and limit mobility. Fortunately, a powerful, modern intervention has emerged: CO₂ cryotherapy. By harnessing the science of cold, this treatment offers swift relief and cellular-level healing. Let’s explore how this innovative therapy stacks up against traditional options.
Understanding Repetitive Strain Syndrome (RSS)
Before exploring solutions, it’s essential to understand what you’re dealing with. RSS isn’t a single condition—it’s a group of disorders with similar underlying causes.
What Is RSS?
Repetitive Strain Syndrome (RSS) is an umbrella term used to describe pain felt in muscles, nerves, and tendons caused by repetitive movement and overuse. It’s commonly seen in office workers, athletes, musicians, and anyone whose job involves repetitive motion. RSS includes conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, tendonitis, and lateral epicondylitis. These injuries often build up gradually over time and can become chronic without intervention. Symptoms include throbbing, tenderness, weakness, and reduced range of motion. Unlike acute injuries, RSS is often subtle at first, but persistent exposure leads to lasting damage. Recognizing the early signs and seeking treatment is key to preventing long-term disability. RSS may seem minor, but its cumulative impact on quality of life and job performance can be profound.
Repetitive Behaviors That Trigger RSS
Repetitive Strain Syndrome (RSS) often stems from seemingly harmless habits that accumulate stress in specific muscles, tendons, or joints. These behaviors are typically part of everyday routines, making them easy to overlook until symptoms arise. Common repetitive actions include:
- Typing or mouse use for prolonged periods without breaks
- Smartphone scrolling or gaming, which strains the thumbs and wrists
- Playing musical instruments, particularly those requiring fine finger movements like violin or piano
- Manual tasks such as cooking, gardening, or lifting objects
- Sports or fitness routines involving repetitive motion (e.g., tennis, rowing, weight training)
- Static posture maintenance, like slouching or leaning forward at a desk
- Performing assembly line or tool-based tasks repeatedly without variation
- Lack of rest and recovery, which prevents tissue repair between sessions
Who’s Most at Risk? Personal and Environmental Factors
While repetitive actions trigger RSS, certain personal characteristics and environmental conditions significantly increase susceptibility. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals and employers take proactive steps to minimize injury risk. Key contributors include:
- Advanced age, which reduces tissue elasticity and healing speed
- Poor physical conditioning, leading to muscle imbalances and fatigue
- Lack of warm-up or stretching routines before repetitive activity
- Pre-existing medical conditions such as arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, or diabetes
- Occupational hazards—factory workers, hairstylists, cashiers, and dental professionals
- Mental stress, contributing to muscle tension and poor posture
- Inadequate ergonomic environments in both home and workplace settings
- Failure to recognize early signs of strain, leading to delayed treatment
CO₂ Cryotherapy: What You Need to Know
With technology advancing, CO₂ cryotherapy is gaining traction as a rapid, drug-free solution for repetitive strain. But what is it, and how does it work?
What Is CO₂ Cryotherapy?
CO₂ cryotherapy uses pressurized carbon dioxide gas, released at -78°C, to rapidly cool targeted areas of the body. The treatment is delivered in brief, controlled bursts of 10 to 15 seconds. This sudden temperature drop stimulates the skin and underlying tissues, triggering a series of physiological responses designed to heal. Unlike traditional ice packs, which cool the skin slowly and unevenly, CO₂ cryotherapy ensures consistent coverage and depth, leading to quicker results. It’s non-invasive, safe when applied correctly, and can be performed in clinics, rehabilitation centers, and even in some home-use settings with proper guidance. For patients with RSS, this method offers a way to break the cycle of inflammation, reduce pain, and speed up recovery—without the side effects of medication or the downtime of surgery.
How It Works Mechanistically
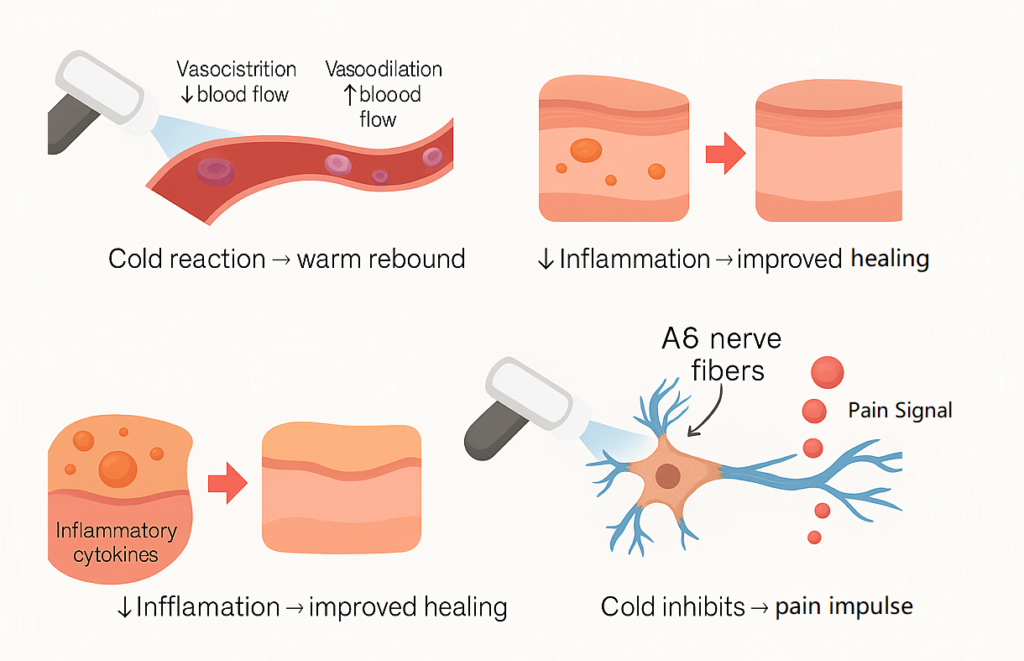
Vasoconstriction and Vasodilation Rebound Effect
The cold blast from CO₂ triggers immediate vasoconstriction—the narrowing of blood vessels. This process minimizes blood flow, reducing inflammation and swelling in the area. But the real magic happens when the treatment ends. As the body warms back up, vasodilation occurs. This widening of blood vessels increases circulation, delivering oxygen and healing nutrients to damaged tissues. It’s this rebound effect—first constricting, then expanding vessels—that stimulates recovery and pain relief. Unlike passive cooling methods, CO₂ cryotherapy initiates a dynamic cycle that not only dulls pain but also enhances cellular repair. For those with RSS, this can mean faster recovery and restored function.
Anti-Inflammatory Response at the Cellular Level
Inflammation is both a symptom and a driver of RSS. CO₂ cryotherapy slows cellular metabolism and reduces the activity of pro-inflammatory mediators such as cytokines. Cold exposure also suppresses immune cell overactivation, which can prolong tissue irritation. On a molecular level, the cold triggers the release of endorphins and reduces oxidative stress—two key factors in pain perception and tissue health. These cellular responses don’t just provide short-term relief—they promote long-term healing. For patients battling chronic inflammation, CO₂ cryotherapy offers a powerful and natural alternative to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can have gastrointestinal and cardiovascular side effects.
How Cold Therapy Alters Pain Perception
Cold therapy impacts the nervous system by slowing down the transmission of pain signals. When CO₂ is applied, the local temperature drop decreases the conductivity of nociceptors—specialized nerve endings that detect harmful stimuli. As these nerves “cool down,” they become less effective at transmitting pain messages to the brain. This neurological disruption results in immediate pain relief. In addition, the release of feel-good chemicals like serotonin and endorphins further blunts discomfort. For individuals with RSS, this means a break from persistent, nagging pain—giving the muscles and joints a chance to rest and recover without constant distress.
Application Techniques for RSS
CO₂ cryotherapy must be applied with precision to maximize benefits and avoid complications. The treatment typically involves a nozzle or handheld device that emits CO₂ gas in a focused spray. The therapist directs the stream over the affected area in sweeping motions, keeping the skin in constant movement to avoid frostbite. Each application lasts around 10–15 seconds per zone, and sessions may involve multiple areas depending on symptom distribution. This technique allows for deep, uniform cooling without damaging the skin. For RSS, focusing on the wrists, forearms, shoulders, or neck (depending on the specific injury) is most effective. Always ensure treatment is conducted by a trained provider, as misuse can lead to burns or insufficient results.
The Science of Cold vs. Heat in Repetitive Strain Recovery
There’s a lot of confusion about whether to use ice or heat for injuries. Let’s break down when each approach is most effective—and how to use both wisely.
When to Use Cold Therapy
Cold therapy is ideal for the acute phase of an injury—within the first 48 to 72 hours after symptoms flare up. During this window, inflammation and swelling are most pronounced. Cold restricts blood flow to the area, slowing the inflammatory response and reducing tissue damage. It also numbs nerve endings, which quickly eases pain. In the case of RSS, where microtraumas build up with repeated use, cold therapy like CO₂ cryotherapy can be used preventatively after periods of high activity. It stops pain before it escalates and promotes faster recovery after strenuous tasks. For chronic RSS, cold therapy can still provide temporary relief during flare-ups, especially when used after intense typing or repetitive labor.
When to Use Heat Therapy
Heat therapy excels in the chronic or recovery phase of an injury. When inflammation subsides but stiffness and limited mobility persist, heat comes into play. By widening blood vessels, heat improves circulation and helps muscles relax. This makes it easier to stretch tight tissues, restore range of motion, and prepare for physical therapy or light activity. For RSS, applying heat before a stretching routine or ergonomic training session can make tissues more pliable and responsive. However, heat should not be applied to areas that are still swollen or acutely painful, as it may worsen inflammation.
Contrast Therapy: Cold Meets Hot
Contrast therapy combines the best of both worlds by alternating between cold and heat. This method stimulates circulation, reduces swelling, and helps flush out metabolic waste from tissues. A typical protocol might include one minute of cold followed by three minutes of heat, repeated for 15–20 minutes. The alternating temperatures cause blood vessels to expand and contract, which pumps fresh blood into the area and supports healing. For chronic RSS sufferers, contrast therapy can be particularly effective in managing persistent symptoms and preventing stiffness. CO₂ cryotherapy can serve as the cold phase in this regimen, offering more targeted and potent effects than ice alone.
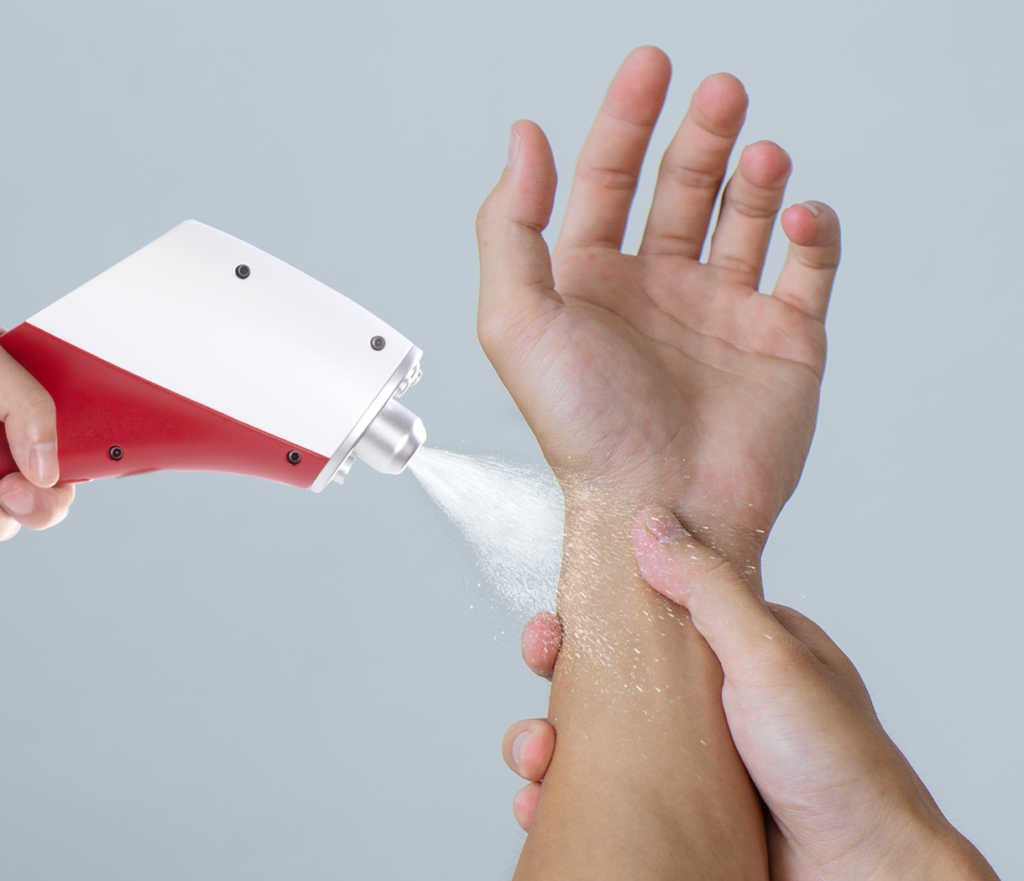

Benefits of CO₂ Cryotherapy for RSS
The appeal of CO₂ cryotherapy lies not only in its modern delivery but also in its wide-ranging benefits. For individuals suffering from Repetitive Strain Syndrome, it offers both immediate relief and long-term healing without the drawbacks of pharmaceuticals or invasive procedures. Let’s dive into the specific advantages.
Immediate Pain Relief Without Medication
One of the standout features of CO₂ cryotherapy is its ability to deliver instant pain relief—without pills, patches, or injections. The ultra-cold spray numbs the skin and underlying nerves, interrupting pain signal transmission to the brain. This numbing effect is almost instantaneous and provides a welcome break from the chronic discomfort that RSS patients often endure. For those wary of side effects associated with NSAIDs or opioids, cryotherapy presents a natural alternative. Moreover, the relief is not just superficial—cryotherapy slows nerve conduction velocity and reduces muscle spasms, which makes it more effective than topical creams or standard ice packs. The fact that it achieves this without sedation or dependency makes it ideal for people who want to stay alert and productive while managing pain.
Reduced Inflammation and Swelling
RSS is often fueled by inflammation—a biological response that, while protective, can become harmful if persistent. CO₂ cryotherapy targets this inflammation head-on by constricting blood vessels and limiting fluid accumulation in affected tissues. The intense cold exposure decreases the activity of inflammatory cytokines and slows cellular metabolism, giving irritated tissues time to recover. As swelling subsides, pressure on nerves and tendons lessens, allowing for greater comfort and movement. For people with visibly swollen joints or muscles, this reduction can be both visually and physically significant. Unlike oral anti-inflammatories, which take time to act and may cause systemic issues, cryotherapy works quickly and locally, precisely where it’s needed most.
Muscle Relaxation and Tissue Recovery
Tight muscles are a common complication of RSS, especially when pain causes guarding or stiffness. CO₂ cryotherapy, while known for its cooling effect, paradoxically helps muscles relax after treatment. Once the cold exposure ends and blood flow rebounds, tissues are flooded with warm, oxygen-rich blood that promotes muscle relaxation and repair. This effect helps flush out waste products like lactic acid, which accumulate during repetitive strain. Additionally, the brief cold shock may reduce the hyperactivity of motor neurons, easing muscle spasms. Whether you’re dealing with aching shoulders, stiff forearms, or tense neck muscles, CO₂ cryotherapy helps restore a sense of ease and flexibility, which is crucial for long-term healing.
Enhanced Mobility and Range of Motion
RSS can severely limit joint mobility and make simple movements painful or awkward. As pain decreases and inflammation subsides through cryotherapy, patients often report improved range of motion. Greater flexibility allows for more effective stretching and rehabilitation exercises, which further accelerate recovery. When combined with ergonomic training or physical therapy, cryotherapy creates an ideal window for retraining muscles and joints to move correctly. By increasing tissue pliability and reducing the sensation of stiffness, CO₂ cryotherapy empowers users to regain lost function and return to normal activity more quickly. For those who rely on fluid movement—such as typists, athletes, or musicians—this benefit is especially valuable.
Better Long-Term Outcomes with Regular Use
While a single cryotherapy session can offer immediate relief, consistent use yields compounding benefits. Regular treatments help maintain lower inflammation levels, keep muscle tension at bay, and prevent symptoms from recurring. For chronic RSS sufferers, incorporating CO₂ cryotherapy into a weekly or bi-weekly wellness routine can dramatically reduce flare-ups and the need for pain medication. It’s especially effective when paired with lifestyle changes like improved ergonomics and mobility exercises. Over time, patients often report fewer disruptions to work and daily life, improved productivity, and better sleep quality. In this way, cryotherapy doesn’t just treat RSS—it helps prevent it from dominating your life again.
Clinical Studies and Scientific Evidence
As with any emerging treatment, credibility is crucial. Fortunately, CO₂ cryotherapy is backed by growing scientific research and real-world outcomes that support its effectiveness in treating repetitive strain and other overuse injuries.
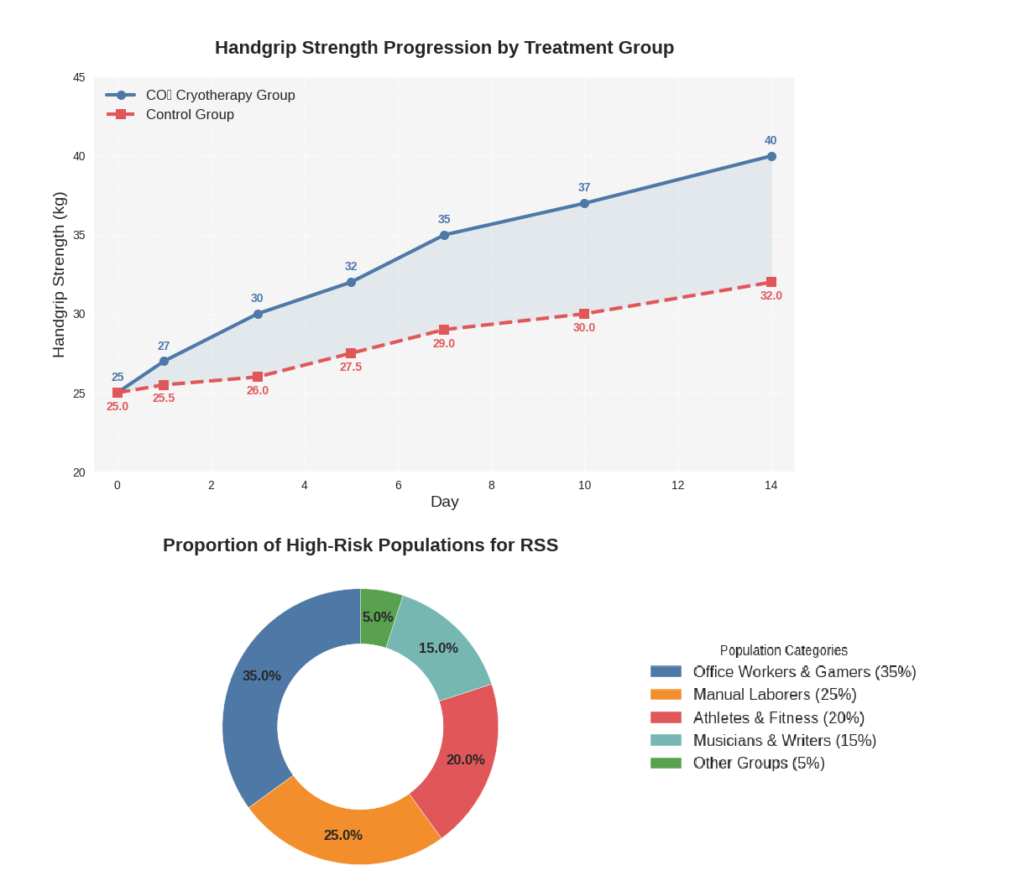
Key Research Supporting Cryotherapy for Overuse Injuries
Numerous studies have highlighted cryotherapy’s role in managing overuse injuries. Research in sports medicine journals consistently shows reduced pain and improved function in athletes who use cold therapy as part of their recovery regimen. Specific studies on localized CO₂ cryotherapy demonstrate significant decreases in inflammatory markers like interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein after treatment. In laboratory tests, patients with tendinopathy or carpal tunnel syndrome have shown improved grip strength and range of motion following a series of cryotherapy sessions. These findings align with anecdotal reports from physical therapists and athletic trainers who regularly use CO₂ cryotherapy as a go-to recovery modality. The evidence is mounting: cold, when applied correctly, accelerates healing.
Comparison with Traditional Therapies
Traditional treatments for RSS include rest, NSAIDs, physiotherapy, bracing, and ergonomic interventions. While effective, these approaches often require long-term compliance and come with potential side effects. NSAIDs, for example, can irritate the stomach lining and raise cardiovascular risks. Bracing may help but can also lead to muscle atrophy with prolonged use. In contrast, CO₂ cryotherapy delivers fast relief without those downsides. It complements physical therapy and can be used preventively without dependency. Unlike heat packs or ultrasound, which primarily affect surface tissues, cryotherapy penetrates deeper layers and triggers systemic healing responses. When used alongside conventional care, it often shortens recovery timelines and improves outcomes.
Safety and Contraindications
While CO₂ cryotherapy is generally safe, it’s not suitable for everyone. Individuals with Raynaud’s disease, cold-induced urticaria, cryoglobulinemia, or poor circulation should avoid cryotherapy unless approved by a healthcare provider. Care must also be taken to avoid frostbite, which can occur if the cryotherapy applicator remains in one spot for too long. Sessions should be administered by trained professionals who understand proper techniques and contraindications. Pregnant individuals, those with heart conditions, or people taking blood thinners should consult their physician before starting treatment. When used correctly, however, the risks are minimal, and the benefits can be substantial.
Who Should Consider CO₂ Cryotherapy?
CO₂ cryotherapy isn’t just for elite athletes—it’s ideal for anyone experiencing the physical toll of repetitive tasks. Whether you’re gaming, hammering, typing, or composing music, your body might benefit from the deep, restorative chill of cold therapy.

Office Workers and Gamers
Sitting at a desk for eight hours a day—or more if you’re gaming—puts strain on the wrists, forearms, neck, and shoulders. Over time, even clicking a mouse or typing becomes a repetitive stressor. Office workers and gamers often develop carpal tunnel syndrome, neck stiffness, and shoulder pain. CO₂ cryotherapy can provide quick relief after long sessions and help prevent symptoms from escalating. Used as a post-work or post-game recovery tool, it helps refresh muscles, reduce inflammation, and preserve hand dexterity. With consistent use, it may even improve reaction time and comfort, which is critical for gamers and remote workers alike.
Manual Laborers and Craftspeople
Construction workers, electricians, hairstylists, and artisans are constantly using their hands and arms in repetitive ways. Lifting, cutting, gripping, and hammering place immense stress on tendons and muscles. These occupations also expose individuals to vibrations and awkward positions, both major contributors to RSS. CO₂ cryotherapy helps these workers bounce back faster between shifts by calming inflamed tissues and reducing stiffness. It’s also useful during midday breaks, providing a quick reset to finish the day strong. For tradespeople who depend on physical precision, the treatment helps keep hands and arms in top condition without relying on painkillers.
Athletes and Fitness Enthusiasts
Athletes regularly push their bodies to the limit, and overuse injuries are almost inevitable—especially in high-repetition sports like tennis, rowing, or weightlifting. CO₂ cryotherapy offers a fast, effective recovery method to manage tendonitis, joint pain, and muscle fatigue. The treatment’s ability to reduce swelling and accelerate tissue repair makes it a staple in athletic recovery programs. Post-training application helps flush out lactic acid and prevent DOMS (Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness), allowing athletes to train harder with less downtime. Whether you’re a weekend warrior or a competitive athlete, cryotherapy can be the missing piece in your performance toolkit.
Musicians and Writers
Repetitive motion injuries don’t spare creatives. Violinists, pianists, drummers, and writers often develop wrist and forearm pain due to long hours of fine-motor activity. Unlike athletes, these individuals may not associate their craft with physical stress—until pain limits their ability to play or type. CO₂ cryotherapy addresses this overlooked population with a gentle, effective treatment that restores dexterity and reduces tension. For musicians preparing for performances or writers racing against deadlines, quick recovery is crucial. Cryotherapy not only reduces pain but enhances precision, ensuring your hands and fingers stay agile and responsive for your art.
Integrating Cryotherapy into Your Recovery Plan
To fully benefit from CO₂ cryotherapy, it should be part of a well-rounded recovery strategy. Used alone, it offers significant relief. But when paired with physical therapy, ergonomic changes, proper nutrition, and clear progress tracking, it becomes a transformative tool in managing Repetitive Strain Syndrome (RSS). Let’s explore how to build a synergistic plan.
Combining CO₂ Cryotherapy with Physical Therapy
Physical therapy and cryotherapy are a powerful duo. While cryotherapy reduces inflammation and dulls pain, physical therapy strengthens muscles, restores mobility, and retrains your body to move properly. When used together, cryotherapy prepares the body for rehab exercises by reducing stiffness and allowing for more comfortable movement. This makes stretching and strengthening routines more effective and reduces the risk of post-exercise flare-ups. Therapists often recommend cryotherapy before or after sessions to enhance outcomes and shorten recovery time. If you’re in a rehab program, consider asking your therapist to coordinate with your cryotherapy provider. This integrative approach not only speeds healing but also lowers the chance of relapse—making your recovery more durable and sustainable.
Workplace Ergonomics and Modifications
Even the best therapy plan can’t succeed if daily habits keep re-injuring your body. That’s where ergonomic modifications come in. If your workspace forces you into awkward angles or repetitive motions, RSS will persist no matter how often you use cryotherapy. Start by adjusting chair height, keyboard placement, and monitor angle to promote neutral posture. Consider investing in an ergonomic mouse, wrist supports, or standing desk if needed. Take regular micro-breaks to stretch and reset your posture throughout the day. CO₂ cryotherapy helps manage symptoms, but ergonomic improvements address the root cause. Together, they break the cycle of injury and make your workspace part of the healing process—not the problem.
Supplements and Nutrition for Healing
Your body’s ability to repair depends heavily on the fuel you give it. To optimize recovery from RSS, pair cryotherapy with nutrition that fights inflammation and supports tissue regeneration. Omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish oil), turmeric, ginger, and magnesium are all known to reduce inflammation. Protein-rich foods help rebuild muscle, while antioxidants in fruits and vegetables protect cells from further damage. Supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin may aid joint health, and collagen supports connective tissue repair. Staying hydrated is equally important, as water helps flush out metabolic waste from damaged tissues. When your internal chemistry supports your external treatments, healing accelerates. Think of nutrition as cryotherapy’s silent partner—essential and often overlooked.
Tracking Progress and Setting Goals
Healing from RSS isn’t always linear, which makes tracking your progress critical. Keeping a simple journal of symptoms, treatment dates, and physical performance can reveal patterns you’d otherwise miss. Are flare-ups less frequent after regular cryotherapy? Is mobility improving after ergonomic adjustments? This data helps you fine-tune your recovery plan and celebrate small wins. Set clear, achievable goals—like reducing pain during a specific activity or increasing typing endurance. Share your goals with your therapist or provider so they can adjust your treatment accordingly. Progress tracking also keeps motivation high, turning recovery into a measurable journey rather than an abstract hope.
Real-World Testimonials and Success Stories
There’s power in hearing from others who’ve been where you are. Across industries—from office cubicles to concert halls—people with RSS have found relief through CO₂ cryotherapy. A graphic designer reported being pain-free after three weeks of regular sessions, while a tennis coach claimed it was the only thing that got him back on the court. One copywriter noted that cryotherapy gave her enough relief to finish her first novel without wrist pain. Athletes use it as a weekly ritual; artisans use it during lunch breaks. These stories highlight how adaptable and effective cryotherapy can be across lifestyles. They also remind us that recovery is possible—often faster than expected—when the right tools are in play.
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
CO₂ cryotherapy is more than just a cold blast—it’s a bold, evidence-backed approach to managing Repetitive Strain Syndrome. It delivers rapid pain relief, reduces inflammation, accelerates muscle recovery, and improves mobility—all without the side effects of drugs. Integrated into a holistic plan involving physical therapy, ergonomic support, and good nutrition, it becomes a cornerstone of lasting recovery. From gamers to gardeners, anyone suffering from repetitive stress can benefit from this powerful technology. Don’t settle for enduring pain—cool it at the source and move freely again.
Key Takeaways:
- Cryotherapy offers fast, drug-free relief for RSS symptoms.
- It works best when combined with rehab, ergonomics, and nutrition.
- Real people from all walks of life have found success with this therapy.
- Long-term use not only treats, but helps prevent re-injury.
FAQs
CO₂ cryotherapy reduces inflammation and numbs pain by rapidly cooling the affected area to approximately -78°C. This triggers vasoconstriction followed by vasodilation (rebound effect), flushing out inflammatory mediators. It also slows nerve conduction, which alters pain perception and reduces muscle spasms—leading to faster recovery and better joint function.
Yes, it’s generally safe when administered by trained professionals. Minor side effects may include temporary redness, numbness, or tingling. Rare risks, such as frostbite or skin burns, are virtually eliminated when the exposure is kept within 10–15 seconds per area and safety protocols are followed.
Many users report immediate symptom relief after just one session. For sustained improvement in chronic RSS, 2–3 sessions per week for 3–4 weeks is often recommended. Results depend on severity, duration of symptoms, and whether cryotherapy is part of a broader treatment plan.
While CO₂ cryotherapy is effective for symptom relief, best outcomes occur when combined with physical therapy, ergonomic changes, and lifestyle adjustments. It addresses inflammation and pain but doesn’t retrain movement patterns or correct posture, which are key in preventing recurrence.
Contraindications include Raynaud’s disease, cold allergies, open wounds, poor circulation, and certain nerve disorders. People with cardiovascular conditions or pregnant individuals should consult a physician first. Always undergo an evaluation before starting treatment.
CO₂ cryotherapy is far more effective due to its ultra-low temperature and rapid application, which deeply penetrates tissues without prolonged exposure. Unlike ice packs, it doesn’t risk skin damage from long use, and its precise application means faster onset of anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.



