Introduction: The Rise of Cryotherapy in Fitness Recovery
The fitness industry has seen a shift in recovery methods, with athletes increasingly turning to advanced solutions like CO₂ cryotherapy. Unlike traditional ice baths and passive rest, CO₂ cryotherapy offers a more sophisticated approach to managing exercise-induced muscle damage (EIMD). This technique combines cutting-edge technology with precise temperature control and targeted treatment areas, addressing multiple recovery needs simultaneously. Its growing popularity stems from the ability to provide controlled, consistent cooling, making it a preferred choice for athletes who need reliable, repeatable results. Unlike static cold treatments, CO₂ cryotherapy allows for timed, targeted treatment of specific muscle groups, making it a powerful tool in post-workout recovery.
Understanding Post-Workout Muscle Soreness
What Causes Muscle Soreness After Exercise?
Post-exercise muscle soreness results from a complex cascade of physiological events initiated by intense physical activity. When muscles contract forcefully or perform unfamiliar movements, microscopic tears occur in muscle fibers, triggering an inflammatory response designed to repair and strengthen the tissue. This process, known as delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS), typically peaks 24-72 hours after exercise. The inflammatory response involves the release of various cytokines, prostaglandins, and other inflammatory mediators that cause pain, swelling, and reduced muscle function. Additionally, metabolic byproducts such as lactate accumulate during intense exercise, contributing to the sensation of muscle fatigue and discomfort. The severity of muscle soreness depends on factors including exercise intensity, duration, muscle groups involved, and individual fitness levels. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing effective recovery strategies that can minimize discomfort while optimizing the adaptive response to training.
Traditional Methods vs. Modern Recovery Techniques
Traditional recovery approaches have primarily focused on passive rest, ice application, and anti-inflammatory medications. Ice packs and cold-water immersion have been standard treatments for decades, operating on the principle that cold temperatures reduce inflammation and numb pain receptors. However, recent research has revealed limitations in these conventional methods. Standard ice application can be inconsistent in temperature delivery, may cause tissue damage if applied too long, and often fails to penetrate deeply enough to affect deeper muscle layers effectively. Cold-water immersion, while more comprehensive, can be uncomfortable and impractical for many individuals. Modern recovery techniques like CO₂ cryotherapy address these limitations through precise temperature control, consistent application, and targeted delivery. These advanced methods offer reproducible results and can be customized to individual needs, making them increasingly popular among professional athletes and fitness enthusiasts seeking optimal recovery outcomes.
CO₂ Cryotherapy for Muscle Recovery: How It Works
The Science Behind CO₂ Cryotherapy
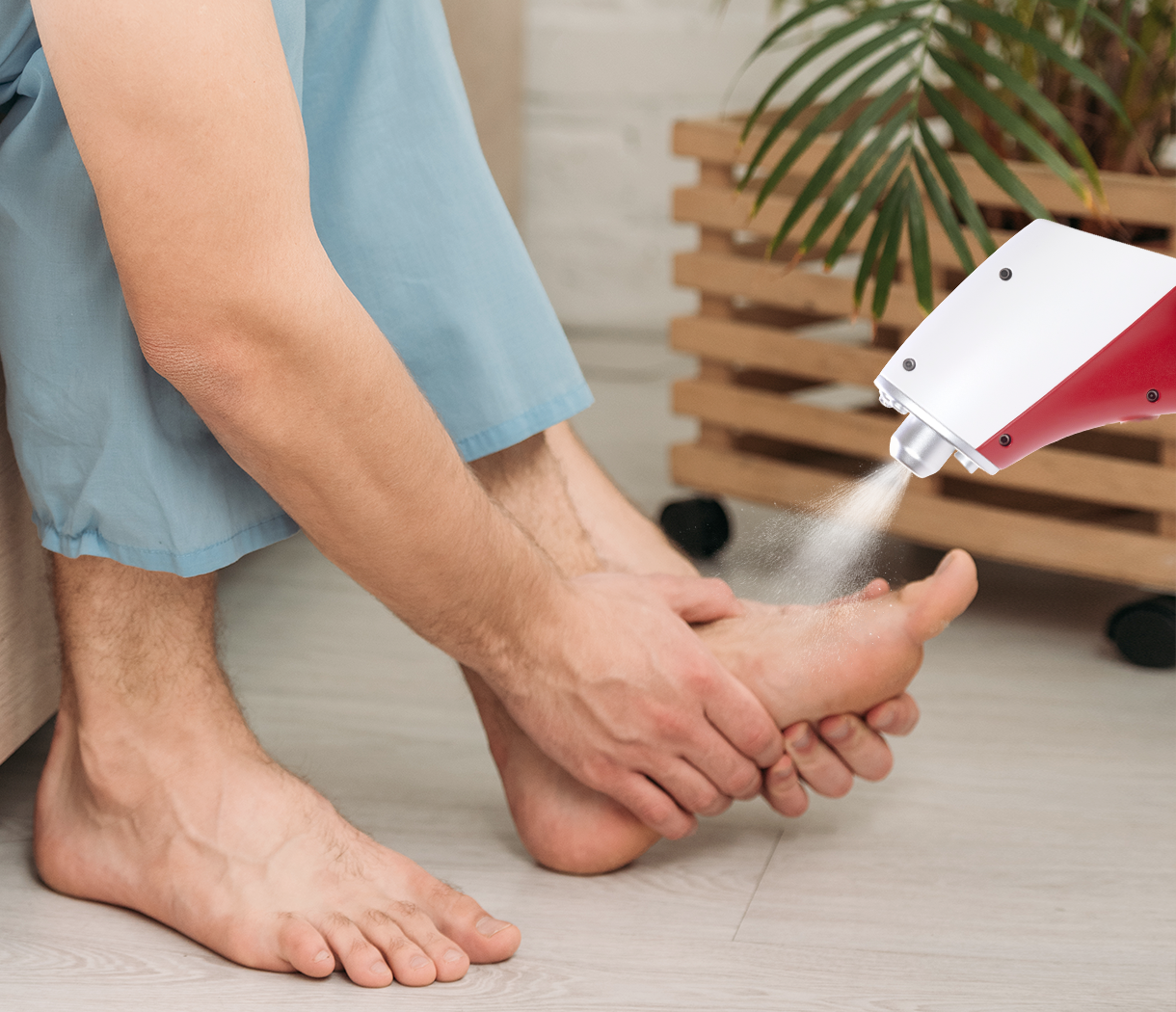
CO₂ cryotherapy utilizes carbon dioxide, commonly known as dry ice, to deliver controlled cooling to targeted areas. When solid CO₂ sublimates, it transforms directly from solid to gas, creating temperatures of approximately -78°C (-108°F). This process provides consistent, predictable cooling that can be precisely controlled for duration and intensity. The mechanism involves the rapid removal of heat from tissue surfaces, creating vasoconstriction in blood vessels and reducing cellular metabolic activity. This controlled cooling triggers a cascade of physiological responses that support muscle recovery and pain reduction. The extreme cold temperature activates cold-sensitive receptors in the skin and underlying tissues, initiating neurological pathways that can modulate pain perception. Unlike traditional ice, CO₂ cryotherapy doesn’t involve moisture, eliminating the risk of frostbite from direct ice contact. The treatment is typically applied for 10-15 seconds per area, allowing for precise control over exposure time and preventing excessive tissue cooling that could impair the healing process.
Immediate Effects on Muscle Pain and Inflammation
The immediate application of CO₂ cryotherapy produces rapid physiological changes that directly impact muscle pain and inflammation. Cold-induced vasoconstriction and reduction of metabolic enzymatic activity lead to limited secondary hypoxic damage to uninjured cells, providing immediate protective effects for stressed muscle tissue. The extreme cold temperature activates the body’s natural analgesic mechanisms through the gate control theory of pain. Large-diameter nerve fibers that respond to cold stimulation can override smaller pain-transmitting fibers, effectively “closing the gate” on pain signals traveling to the brain. This results in immediate pain relief that can last for several hours post-treatment. Additionally, the rapid cooling reduces the activity of inflammatory enzymes and decreases the production of inflammatory mediators. This anti-inflammatory effect helps limit the extent of secondary tissue damage that can occur following intense exercise, potentially reducing both the severity and duration of muscle soreness.
Boosting Blood Circulation and Oxygen Delivery
Following the initial vasoconstriction phase, CO₂ cryotherapy triggers a robust vasodilation response as tissues rewarm. This reactive hyperemia significantly increases blood flow to the treated area, enhancing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients essential for muscle repair and recovery. The enhanced circulation facilitates the removal of metabolic waste products that accumulate during exercise, including lactate, creatine kinase, and other inflammatory byproducts. This improved clearance of metabolic waste helps reduce muscle fatigue and accelerates the return to normal muscle function. The benefits include increased circulation, reduced inflammation, increased mitochondrial activity, and enhanced tissue repair, creating an optimal environment for muscle recovery. The improved oxygen delivery also supports cellular energy production, helping muscles recover their contractile capacity more quickly than with passive recovery methods alone.
Enhancing Performance and Reducing Downtime
The systematic application of CO₂ cryotherapy can lead to measurable improvements in recovery time and subsequent performance. Cryotherapy with CO₂ promotes greater immediate recovery of muscle power from neuromuscular fatigue compared with traditional ice or passive rest, making it particularly valuable for athletes with frequent training sessions. The reduced inflammation and accelerated healing process allow athletes to return to training sooner with less residual muscle soreness. This shortened recovery period is crucial for maintaining training consistency and progressive overload, key factors in athletic development and fitness improvement. Regular use of CO₂ cryotherapy may also contribute to improved adaptation to training stress. By optimizing the recovery process, muscles can more effectively respond to training stimuli, potentially leading to enhanced strength, endurance, and overall performance gains over time.
Why Your Muscles Love It: Proven Benefits After Exercise
Reducing Inflammation and Muscle Microtrauma
CO₂ cryotherapy’s primary benefit lies in its ability to modulate the inflammatory response following exercise-induced muscle damage. The controlled cooling creates an environment that reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines while preserving the beneficial aspects of the healing response. Cryotherapy reduces inflammatory response without altering muscle regeneration process, ensuring that recovery is accelerated without compromising the adaptive benefits of exercise. This selective anti-inflammatory effect is crucial for maintaining the balance between recovery and adaptation. The treatment specifically targets muscle microtrauma by reducing secondary tissue damage that can occur when inflammatory responses become excessive. By controlling this inflammatory cascade, CO₂ cryotherapy helps minimize pain and swelling while preserving the cellular mechanisms necessary for muscle strengthening and repair.
Enhanced Blood Circulation for Faster Healing
The vascular response to CO₂ cryotherapy creates significant improvements in local blood circulation that persist well beyond the treatment session. This enhanced circulation provides sustained benefits for muscle recovery by maintaining elevated nutrient and oxygen delivery to recovering tissues. Improved circulation also supports the lymphatic system’s ability to remove inflammatory debris and metabolic waste products from muscle tissue. This enhanced clearance mechanism helps reduce tissue swelling and accelerates the resolution of exercise-induced inflammation. The combination of improved arterial inflow and enhanced venous and lymphatic drainage creates optimal conditions for tissue healing. This circulatory enhancement is particularly beneficial for deep muscle tissues that may not receive adequate blood flow during passive recovery methods.
Relief from Muscle Soreness and Fatigue
The neurological effects of CO₂ cryotherapy provide both immediate and sustained relief from muscle soreness and fatigue. The activation of cold receptors creates powerful analgesic effects that can significantly reduce pain perception for hours following treatment. The primary benefit of cryotherapy is reduced pain following injury or soreness following exercise, making it an effective tool for managing post-workout discomfort. This pain relief allows individuals to maintain normal daily activities and potentially engage in light recovery activities that further support the healing process. The reduction in perceived muscle fatigue also has psychological benefits, improving motivation and confidence for subsequent training sessions. This psychological component of recovery is often overlooked but plays a crucial role in maintaining consistent training habits and long-term athletic development.
Supporting Athletic Performance Over Time
Regular application of CO₂ cryotherapy as part of a comprehensive recovery protocol can lead to cumulative performance benefits. By consistently optimizing the recovery process, athletes can maintain higher training volumes and intensities over time, leading to greater long-term adaptations. Cryotherapy may provoke changes in neurotransmitters like dopamine and increase activity between the sympathetic nervous system and skeletal muscle, potentially providing performance-enhancing effects beyond simple recovery. These neurological adaptations may contribute to improved muscle activation and coordination. The ability to train more frequently with reduced soreness allows for greater training consistency, which is fundamental to athletic improvement. This enhanced training capacity, combined with optimized recovery, creates a positive cycle that can lead to significant performance gains over months and years of consistent application.
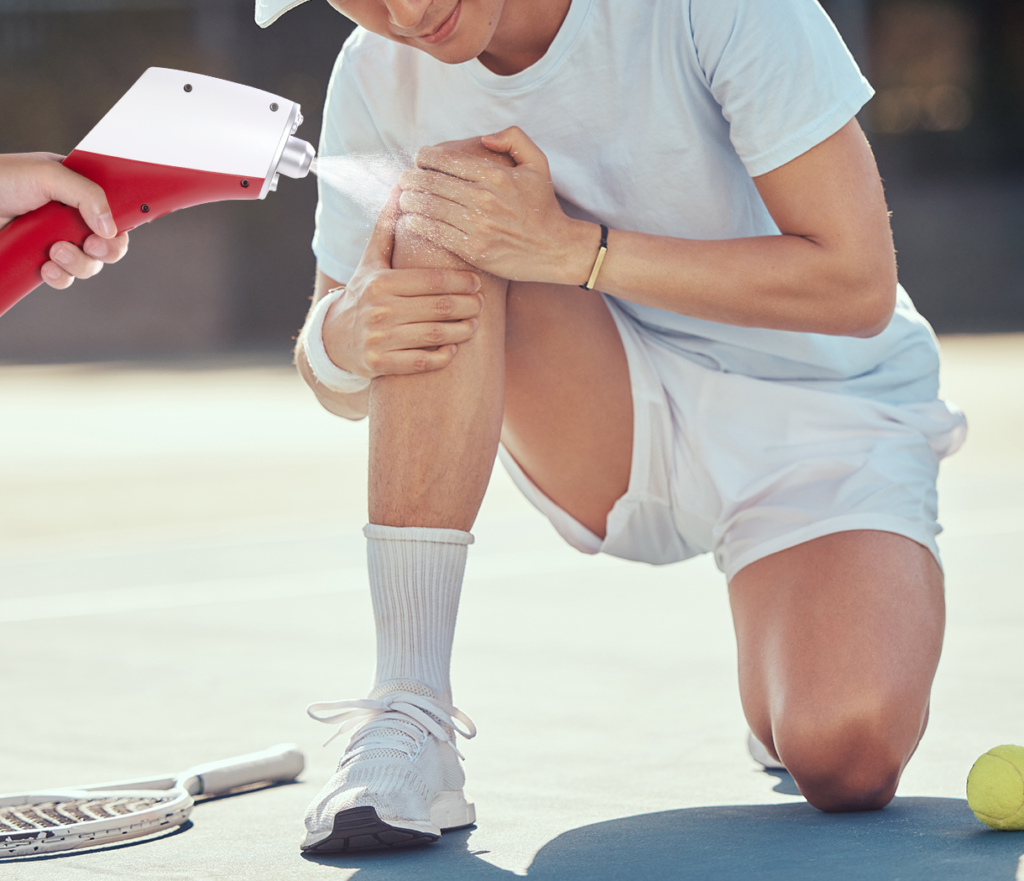

Is CO₂ Cryotherapy Safe and Suitable for You?
Ideal Candidates for Post-Workout Cryo
- Athletes and Fitness Enthusiasts: Ideal for individuals who engage in intense training or competition.
- Those with Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS): Effective for alleviating soreness after rigorous workouts.
- People Experiencing Inflammation or Fatigue: Helps reduce inflammation and muscle fatigue.
- Individuals Prone to Muscle Strains or Joint Pain: Beneficial for those recovering from minor injuries.
- High-Impact Sports Participants: Especially helpful for runners, weightlifters, CrossFit athletes, or those in contact sports.
- Performance-focused Individuals: Great for those looking to speed up recovery and enhance overall performance.
- Health Considerations: Not recommended for individuals with severe cardiovascular issues without medical consultation. Always seek professional advice before use.
Safety Considerations and Contraindications
While CO₂ cryotherapy is generally safe when properly administered, certain individuals should exercise caution or avoid the treatment entirely. People with cardiovascular conditions, including hypertension, heart disease, or circulation disorders, should consult with healthcare providers before beginning cryotherapy treatments. Individuals with cold sensitivity disorders, such as Raynaud’s disease or cold urticaria, may experience adverse reactions to extreme cold exposure. Pregnant women and individuals with certain skin conditions or open wounds in treatment areas should also avoid CO₂ cryotherapy until these conditions resolve. Proper application technique is crucial for safety, with treatment duration typically limited to 10-15 seconds per area to prevent tissue damage. Professional supervision or proper training in application techniques is recommended to ensure safe and effective treatment outcomes.
How to Integrate CO₂ Cryo into Your Gym Routine
When to Use CO₂ Cryotherapy: Timing Matters
The timing of CO₂ cryotherapy application significantly influences its effectiveness for muscle recovery. Optimal timing typically falls within the first few hours following intense exercise, when inflammatory processes are most active and responsive to intervention. Immediate post-workout application, within 15-30 minutes of exercise completion, can provide maximum anti-inflammatory benefits by intervening early in the inflammatory cascade. This timing helps prevent excessive inflammation while preserving beneficial adaptive responses to exercise stress. For individuals experiencing delayed onset muscle soreness, CO₂ cryotherapy can be applied 24-48 hours post-exercise when soreness typically peaks. This delayed application can provide significant pain relief and accelerate the resolution of lingering muscle discomfort from previous training sessions.
How Often Should You Use Cryotherapy
The frequency of CO₂ cryotherapy application should be tailored to individual training schedules, recovery needs, and response to treatment. For athletes with daily training sessions, cryotherapy can be applied after each intense workout, particularly those involving high-intensity or eccentric muscle contractions. Recreational exercisers may benefit from cryotherapy 2-3 times per week, focusing on sessions following the most challenging or unfamiliar exercises. This frequency allows for adequate recovery while preventing potential adaptation interference from excessive anti-inflammatory intervention. Monitoring individual response to treatment is crucial for determining optimal frequency. Factors such as muscle soreness reduction, improved sleep quality, and enhanced subsequent training performance can guide adjustments to treatment frequency and ensure maximum benefit from the therapy.
Conclusion: Cool Your Muscles, Fire Up Your Recovery
CO₂ cryotherapy represents a significant advancement in post-exercise recovery technology, offering precise, effective, and convenient muscle recovery enhancement. The scientific evidence supporting its use continues to grow, with research demonstrating clear benefits for pain reduction, inflammation control, and accelerated recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage. The integration of CO₂ cryotherapy into fitness recovery protocols can provide measurable improvements in training consistency, reduced downtime, and enhanced overall performance. As our understanding of exercise physiology and recovery mechanisms continues to evolve, targeted interventions like CO₂ cryotherapy will likely play increasingly important roles in optimizing athletic performance and fitness outcomes. For individuals serious about their fitness goals and recovery optimization, CO₂ cryotherapy offers a scientifically-backed, practical solution that can complement existing recovery strategies. When properly implemented and combined with adequate nutrition, hydration, and sleep, this technology can help unlock new levels of training capacity and performance potential.
FAQ: CO₂ Cryotherapy After Workouts
A: Individual treatment areas typically receive 10-15 seconds of CO₂ application. A complete session targeting multiple muscle groups usually takes 5-10 minutes, making it highly convenient for post-workout routines.
A: CO₂ cryotherapy offers several advantages over ice baths, including precise temperature control, targeted application, and dry cooling that eliminates frostbite risks. Research suggests it may provide superior immediate recovery benefits compared to traditional ice treatments.
A: Daily use is generally safe for healthy individuals, particularly athletes with frequent training sessions. However, frequency should be adjusted based on individual response and training demands to optimize recovery benefits without interfering with adaptation.
A: Side effects are rare when properly applied. Some individuals may experience temporary skin redness, numbness, or cold sensitivity immediately following treatment. These effects typically resolve within minutes of treatment completion.
A: Optimal timing is within 15-30 minutes post-exercise for maximum anti-inflammatory benefits. However, effective results can still be achieved when applied several hours after exercise or during peak soreness periods 24-48 hours later.



