CO₂ cryotherapy is recognized for its ability to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and support healing. However, when experiencing cold symptoms, the decision to undergo treatment becomes more complex. Factors like immune response and the body’s natural recovery must be considered. This examination delves into the relationship between cryotherapy and cold symptoms, exploring scientific evidence and clinical considerations to help individuals make informed decisions about the timing and safety of treatment during illness. The goal is to understand when cryotherapy can be beneficial and how to balance its advantages with potential risks during viral infections like the common cold.
Introduction: Understanding CO₂ Cryotherapy and Cold Symptoms
The growing popularity of cryotherapy has led many to question its safety and effectiveness during a cold. This treatment intersects with viral infections, requiring an understanding of both cryotherapy’s effects and immune system changes during illness. Cold symptoms create physiological shifts that may affect the body’s response to extreme cold. Immune activation, inflammation, and circulatory changes could impact cryotherapy’s safety and efficacy, making professional advice crucial for the best results.
CO₂凍結療法とは?
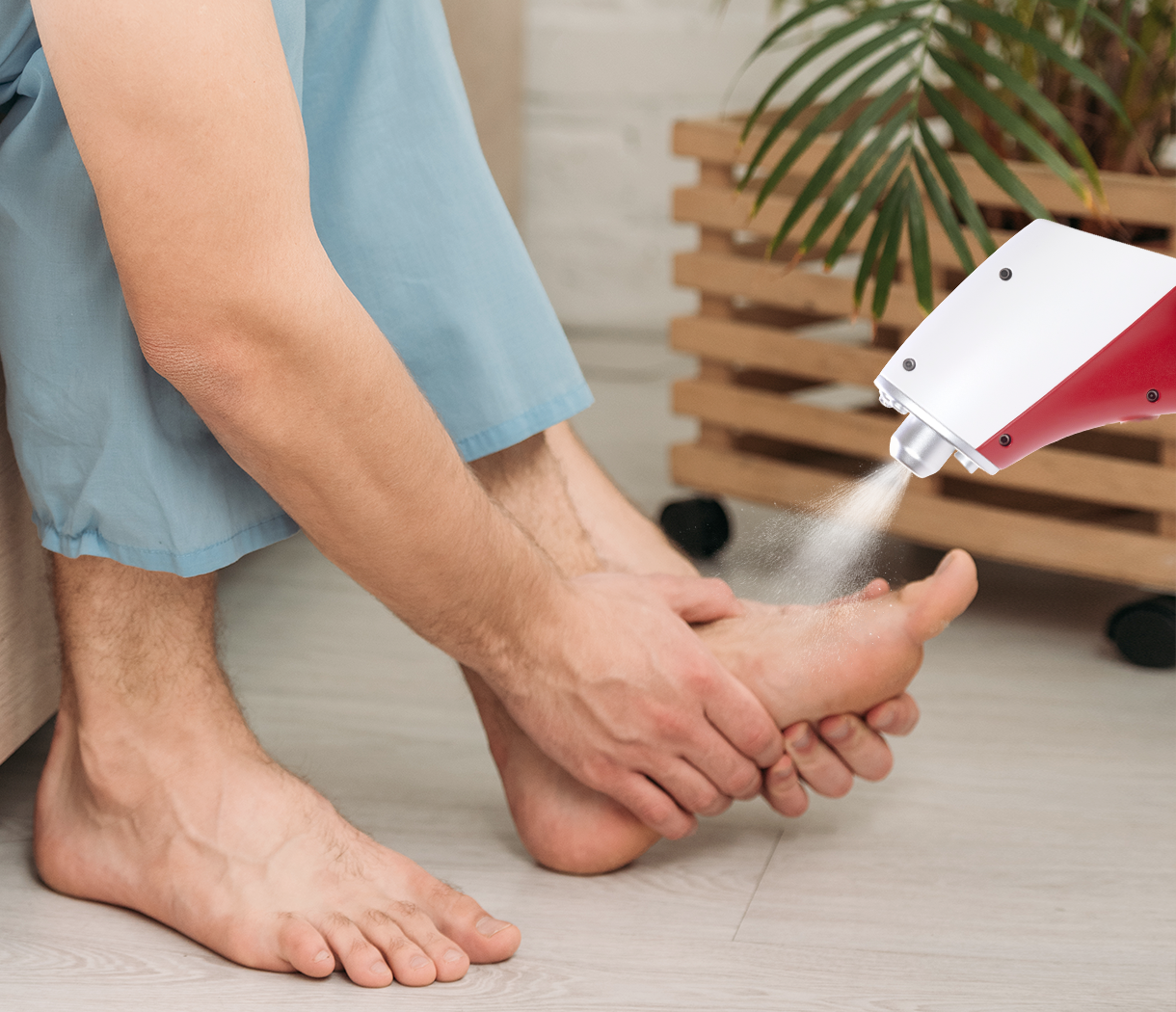
CO₂ cryotherapy represents an advanced form of localized cold therapy that utilizes pressurized carbon dioxide gas to deliver precise, controlled cooling to specific areas of the body. This therapeutic modality operates by releasing CO₂ at extremely low temperatures, typically reaching -78°C (-108°F), creating an immediate thermal shock that triggers multiple physiological responses. The treatment duration is typically brief, lasting approximately 10-15 seconds per application, making it both efficient and well-tolerated by most individuals. The mechanism involves the rapid expansion of pressurized CO₂ gas, which creates an intense cooling effect that penetrates deeper into tissues compared to traditional ice therapy. This controlled thermal shock triggers vasoconstriction, reduces nerve conduction velocity, and initiates the body’s natural anti-inflammatory responses. The precision of CO₂ delivery allows practitioners to target specific anatomical areas with remarkable accuracy, often enhanced by red laser guidance systems that ensure optimal treatment placement and effectiveness.
What Happens When You Have a Cold?
The common cold, primarily caused by rhinovirus infections, initiates a complex cascade of immune responses designed to eliminate the viral pathogen and restore normal physiological function. During the initial stages of infection, the immune system activates inflammatory pathways, increasing cytokine production and promoting vasodilation in nasal passages and respiratory tissues. This inflammatory response manifests as familiar symptoms including nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, sore throat, and general malaise. The body’s systemic response to viral infection involves increased metabolic demands, elevated core body temperature regulation, and heightened immune surveillance activity. These physiological changes affect circulation patterns, thermoregulatory mechanisms, and overall stress responses, creating a state of increased vulnerability to external stressors. Additionally, the inflammatory mediators released during cold infections can influence pain perception, tissue sensitivity, and recovery processes, factors that may interact with cryotherapy treatment effects and outcomes.
The Impact of Cryotherapy on the Body
Cryotherapy triggers a range of physiological responses, impacting immune function, inflammation, and overall homeostasis. Its immediate and delayed effects extend beyond local responses, influencing neurological, vascular, and hormonal systems. These multisystem effects contribute to its therapeutic benefits but must be carefully considered, especially for individuals with compromised immune systems or ongoing illness. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for assessing the safety and efficacy of cryotherapy during illness.
CO₂クライオセラピーの仕組み
CO₂ cryotherapy operates through the principle of controlled thermal shock, delivering rapid cooling that creates immediate physiological changes in treated tissues. The extreme temperature differential between normal body temperature and the -78°C CO₂ application triggers immediate vasoconstriction, reducing blood flow to the treated area and minimizing inflammatory responses. This rapid cooling also significantly slows nerve conduction velocity, effectively interrupting pain signal transmission and providing immediate analgesic effects. The cellular-level effects of CO₂ cryotherapy include reduced metabolic activity in treated tissues, decreased enzyme activity, and modified membrane permeability. These changes contribute to reduced inflammation, minimized tissue damage, and enhanced healing processes. The brief treatment duration prevents tissue damage while maximizing therapeutic benefits, making this modality particularly suitable for localized pain management and inflammation control. The precision of CO₂ delivery ensures that surrounding healthy tissues remain unaffected while maximizing therapeutic impact in target areas.
Cryotherapy’s Effect on the Immune System
Cryotherapy influences immune function by reducing inflammation and potentially boosting immunity through controlled cold exposure. Research shows that brief cold exposure has beneficial effects, stimulating immune responses by increasing white blood cell activity and cytokine release. However, prolonged exposure may have immunosuppressive effects. CO₂ cryotherapy, with its controlled cold application, typically falls within the beneficial range, supporting the immune system. Despite common belief, brief cold exposure does not negatively affect the innate immune system, even during viral infections. The timing and intensity of cryotherapy’s effects can vary based on immune activation, such as during a cold. While cold exposure may help activate the immune system, its impact during illness should be considered carefully to avoid adding unnecessary stress to the body’s healing process.
Does CO₂ Cryotherapy Influence Nasal and Sinus Health?
Cryotherapy’s effects on nasal and sinus health involve complex interactions between cold exposure, blood flow, and mucosal function. Localized cold application can influence blood flow in the nasal passages, potentially affecting mucus production and drainage. The vasoconstrictor effects of cryotherapy may provide temporary relief from nasal congestion by reducing swelling in nasal tissues. However, this effect must be balanced with its impact on mucus clearance and natural drainage processes. The proximity of cryotherapy to respiratory structures requires careful attention to treatment sites and intensity to avoid adverse effects on already compromised functions. For individuals with active sinus infections or severe congestion, the response to cryotherapy may be altered due to existing inflammation and tissue sensitivity. Overall, while cryotherapy may offer temporary relief, its effects on respiratory function during illness should be carefully evaluated.
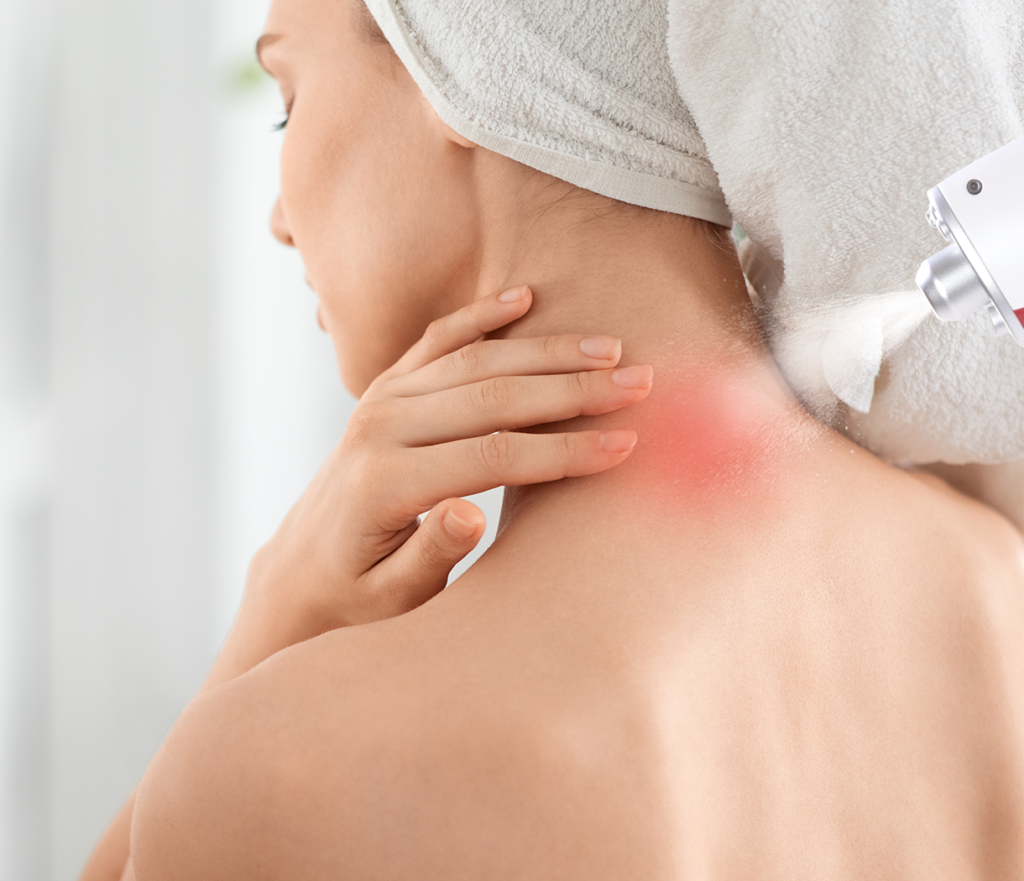
Is It Safe to Undergo CO₂ Cryotherapy During a Cold?
The safety of CO₂ cryotherapy during cold symptoms depends on factors like symptom severity, health status, and treatment parameters. While generally safe, active illness introduces additional considerations. A professional assessment is essential to evaluate individual responses, immune status, and overall health. Balancing potential benefits with risks ensures optimal treatment decisions and patient safety, especially during viral infections. Understanding these dynamics helps inform when cryotherapy is appropriate and safe.
General Precautions for Cryotherapy During Illness
When considering cryotherapy during illness, several precautions must be observed to ensure patient safety and treatment effectiveness. Individuals with active infections, including common colds, may experience altered physiological responses to extreme cold exposure due to changes in immune function, circulation patterns, and thermoregulatory mechanisms. These alterations can potentially modify treatment outcomes and may increase the risk of adverse reactions or complications. Temperature regulation may be compromised during illness, particularly when fever is present, making the body less able to adapt to extreme temperature changes. Additionally, medications commonly used to treat cold symptoms, such as decongestants or antihistamines, can affect cardiovascular responses and may interact with the physiological effects of cryotherapy. Hydration status, which is often compromised during illness, also influences the body’s ability to respond appropriately to thermal stress. These factors necessitate careful evaluation and possible treatment modifications to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Cryotherapy When You Have a Cold
Exacerbation of Respiratory Issues: Cryotherapy may worsen nasal or sinus congestion, especially in individuals with respiratory issues.
Bronchospasm Risk: Cold exposure may trigger bronchospasm in susceptible individuals with respiratory conditions.
Immune System Stress: Extreme cold exposure can put additional strain on an already activated immune system.
Altered Circulatory Response: Cold symptoms may change vascular responses, potentially affecting treatment efficacy or increasing risks.
Perception of Cold: Nasal congestion can reduce cold sensation perception, affecting treatment comfort and outcomes.
Fatigue and Recovery Delays: Cryotherapy combined with illness-related fatigue may lead to increased exhaustion or prolonged recovery.
When Cryotherapy Might Be Beneficial During a Cold
Mild Cold Symptoms: Cryotherapy may provide relief and immune support, helping with localized pain or inflammation.
Localized Pain Relief: If cold symptoms are mild, cryotherapy can address pain unrelated to the cold without interfering with recovery.
Anti-inflammatory Effects: Cryotherapy’s anti-inflammatory benefits can support the body’s natural healing, particularly for musculoskeletal pain.
Targeted Treatment: The localized nature of CO₂ cryotherapy minimizes systemic effects, making it suitable for mild symptoms.
Factors to Consider Before Undergoing CO₂ Cryotherapy While Sick
The decision to undergo cryotherapy during illness requires careful evaluation of individual factors such as health status, medications, and risk factors. This goes beyond simple symptom assessment to ensure both safety and effectiveness. Professional evaluation is especially important during illness, as the interaction between cryotherapy and disease processes can be complex. A systematic approach to assessing these factors helps make informed treatment decisions and ensures optimal outcomes. Understanding how individual health conditions and treatment effects interact allows for appropriate adjustments to be made, ensuring the treatment is both safe and effective.
Severity of Cold Symptoms
The severity and stage of cold symptoms are key factors in determining whether cryotherapy is appropriate. Mild symptoms like slight nasal congestion or minor fatigue may not rule out treatment, especially for issues like musculoskeletal pain. However, moderate to severe symptoms such as significant congestion, fever, or systemic malaise usually require postponing cryotherapy until recovery. The acute phase of illness, marked by peak immune activation and stress, may make cryotherapy poorly tolerated and could hinder recovery. In contrast, individuals in the early recovery phase with minimal symptoms may be better candidates for cryotherapy, provided treatment is carefully monitored. Decisions should be based on symptom progression, illness duration, and individual tolerance to determine the best time for treatment.
Personal Health and Medical Conditions
Individual health status and underlying medical conditions significantly influence the safety profile of cryotherapy during illness. Individuals with compromised immune systems, chronic respiratory conditions, cardiovascular disease, or autoimmune disorders may be at increased risk for complications when combining cold exposure with active illness. These conditions can affect the body’s ability to mount appropriate physiological responses to thermal stress and may alter recovery patterns from both illness and treatment. Age-related factors also play important roles, as older adults and very young individuals may have reduced thermoregulatory capacity and altered immune responses that affect treatment safety during illness. Additionally, individuals taking medications that affect circulation, immune function, or temperature regulation may experience modified responses to cryotherapy. Pregnancy, diabetes, and peripheral vascular disease are additional conditions that require special consideration when evaluating treatment appropriateness during periods of illness. These factors necessitate thorough medical history review and professional consultation before proceeding with treatment.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial before undergoing cryotherapy during illness. A medical provider can assess individual risk factors, symptom severity, and recommend treatment modifications tailored to specific circumstances. This is especially important for those with underlying health conditions or taking medications that may interact with cryotherapy. Professionals can also determine the best timing for cryotherapy, advising when it’s safe to resume treatment after illness based on recovery progress and residual symptoms. They ensure that treatment decisions are guided by a comprehensive medical evaluation, reducing risks and optimizing outcomes.
Alternatives to CO₂ Cryotherapy When You Have a Cold
When cryotherapy is not suitable due to cold symptoms or other health concerns, several alternatives can offer pain relief and reduce inflammation. These options provide similar benefits without the risks of cold exposure during immune activation. Understanding these alternatives ensures continuity of care and symptom management when primary treatments need to be postponed. For individuals with chronic pain and concurrent illness, these alternatives allow for continued symptom management without interfering with recovery. Choosing the right alternative depends on specific symptoms, underlying conditions, and individual treatment goals.
Other Recovery Treatments for Cold Symptoms
Heat therapy represents a primary alternative to cold treatment during illness, offering complementary benefits such as improved circulation, muscle relaxation, and enhanced comfort. Warm compresses, heating pads, or warm baths can provide localized pain relief while supporting overall comfort during cold recovery. The vasodilation effects of heat therapy can also help improve circulation and support natural healing processes without the physiological stress associated with extreme cold exposure. Gentle massage therapy, when appropriate, can provide muscle relaxation and stress relief while supporting lymphatic drainage and circulation. Topical analgesics or anti-inflammatory medications may offer localized pain relief without systemic effects that might interfere with immune function. Rest, hydration, and gentle stretching exercises can support overall recovery while addressing musculoskeletal discomfort. These approaches allow for symptom management while prioritizing immune system recovery and overall health during illness.
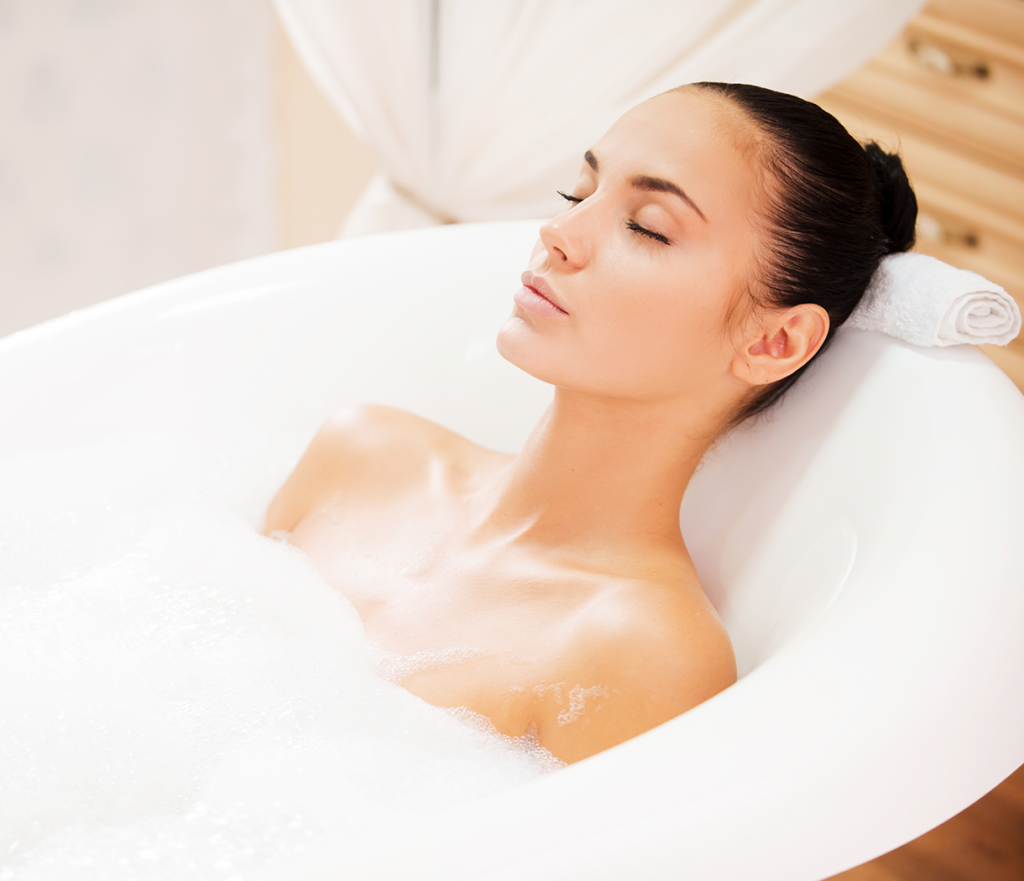

When to Opt for Cryotherapy Post-Recovery
The timing for resuming cryotherapy treatments following illness recovery requires careful consideration of multiple factors to ensure optimal safety and effectiveness. Generally, individuals should be completely symptom-free for at least 24-48 hours before resuming elective treatments, allowing sufficient time for immune system recovery and physiological normalization. This waiting period helps ensure that the body has adequate reserves to respond appropriately to treatment stress. Complete resolution of symptoms including congestion, cough, fatigue, and any systemic signs of illness should be achieved before considering treatment resumption. Additionally, individuals should feel that their energy levels and overall well-being have returned to baseline levels. For those with underlying health conditions or prolonged illness, longer waiting periods may be appropriate, and professional medical clearance may be advisable before resuming treatments. The gradual return to normal activities and exercise tolerance can serve as indicators of readiness for therapeutic interventions.
Final Thoughts on Cryotherapy During Illness
Deciding whether to undergo CO₂ cryotherapy during a cold requires balancing potential benefits and risks, along with professional guidance. While mild symptoms might not necessarily rule out treatment, it is generally advised to wait until full recovery. This conservative approach ensures immune function is prioritized while minimizing complications. Cryotherapy’s brief cold exposure can enhance circulation, reduce inflammation, and boost immunity, but these benefits must be considered against the added stress of illness. Factors like symptom severity, overall health, and treatment goals influence the decision. Professional consultation is crucial to evaluate individual circumstances and determine whether adjustments or alternatives are necessary. Ultimately, the goal is to support health and well-being safely while achieving treatment objectives effectively.
FAQs About Cryotherapy and Illness
Cryotherapy may stimulate the immune system, but during illness, the immune system is already activated. Extra stress may not offer the same benefits, and the risk of exacerbating symptoms should be considered.
Wait 24-48 hours after all symptoms have resolved. For those with health conditions or slow recovery, waiting 3-5 days may be necessary. Consult a professional to determine the best timing.
Cryotherapy may temporarily reduce congestion by constricting blood vessels but doesn’t address underlying viral causes. Traditional treatments like saline rinses may be more effective.
Risks include worsening respiratory symptoms, stressing the immune system, and interfering with recovery. Altered responses to cold or medications may increase the chance of frostbite or complications. Always seek professional guidance.



