Introduction: Understanding Localized Pain and Swelling
Pain and inflammation represent two of the most common reasons individuals seek medical attention. Whether resulting from acute injury, chronic conditions, or post-operative recovery, these symptoms significantly impact quality of life and functional capacity. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of pain and swelling is essential for appreciating how targeted therapeutic interventions can provide rapid, effective relief.
What is Localized Pain?
Localized pain refers to nociceptive sensations confined to a specific anatomical region rather than diffused throughout the body. This type of pain originates from peripheral nociceptors—specialized sensory neurons that detect potentially harmful stimuli and transmit signals through the dorsal root ganglia to the central nervous system. Unlike systemic or referred pain, localized discomfort allows for precise identification of the affected area, making it particularly amenable to targeted therapeutic interventions. Common examples include joint pain, muscle soreness, and post-traumatic tenderness.
Common Causes of Swelling and Inflammation
Inflammation represents the body’s protective response to tissue damage, infection, or irritation. The classic signs—rubor (redness), calor (heat), tumor (swelling), dolor (pain), and functio laesa (loss of function)—result from increased vascular permeability and inflammatory mediator release. Acute inflammation typically follows trauma, repetitive strain injuries, or surgical procedures, while chronic inflammatory conditions include osteoarthritis, tendinitis, and bursitis. The accumulation of interstitial fluid, known as edema, contributes significantly to both discomfort and restricted mobility in affected areas.
Importance of Effective and Fast Relief
Timely intervention for pain and inflammation is crucial not only for comfort but also for preventing secondary complications. Prolonged inflammation can lead to tissue fibrosis, chronic pain sensitization, and delayed functional recovery. Traditional approaches often rely on pharmacological interventions, which may present contraindications, adverse effects, or delayed onset of action. Non-invasive, rapid-acting modalities that address both pain and swelling simultaneously offer significant advantages, particularly for athletic populations, elderly patients, and individuals seeking drug-free alternatives for musculoskeletal conditions.
Что такое криотерапия CO₂?
As medical technology advances, therapeutic approaches increasingly emphasize precision, safety, and efficiency. CO₂ cryotherapy represents a sophisticated evolution of traditional cold therapy, harnessing the unique properties of pressurized carbon dioxide to deliver targeted, controlled cooling with remarkable therapeutic outcomes.
Definition and Basic Principles of CO₂ Cryotherapy
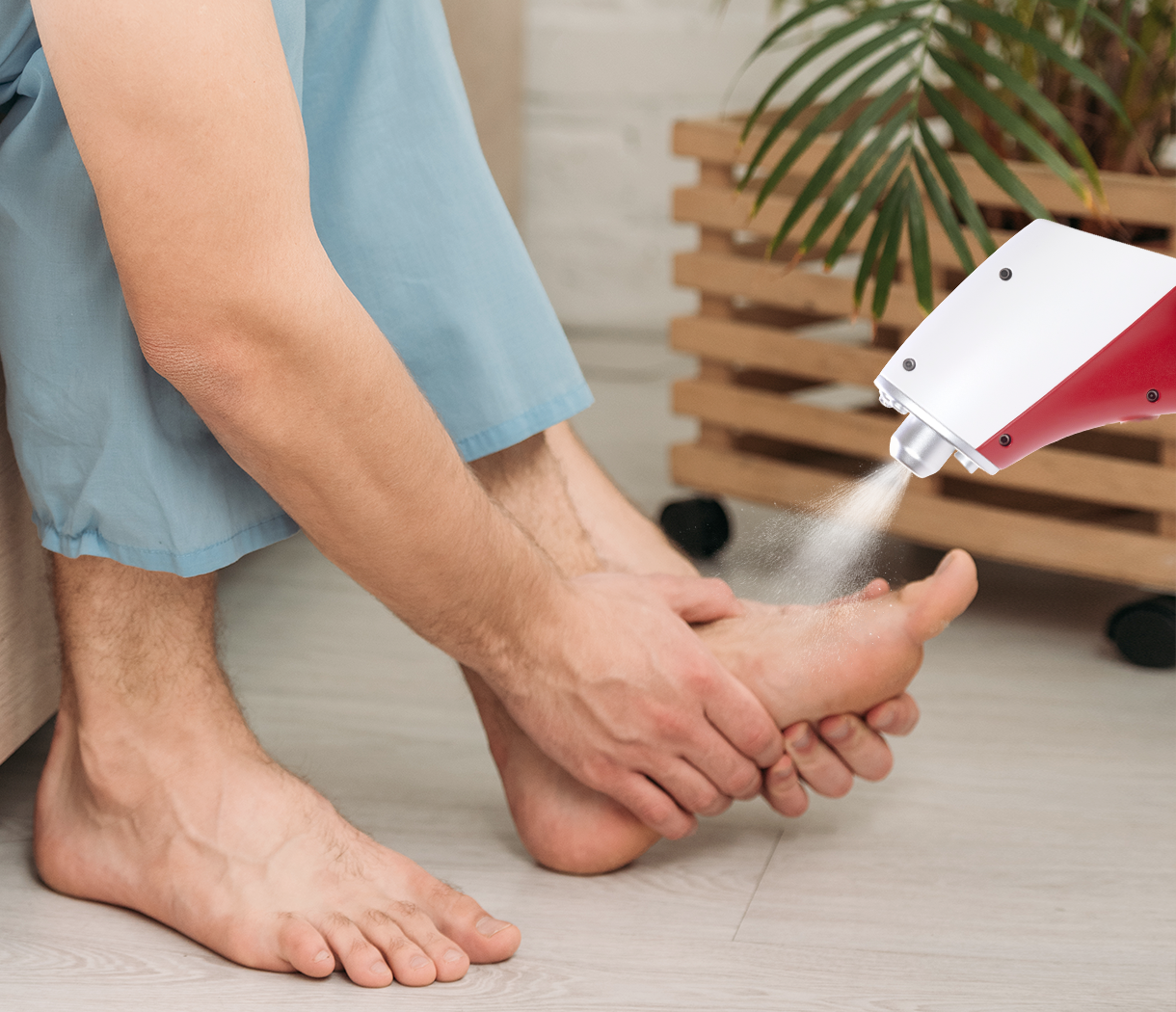
CO₂ криотерапия utilizes pressurized carbon dioxide gas, which is released at temperatures reaching -78°C (Celsius), to create a rapid thermal shock on targeted tissue surfaces. This controlled cryogenic application exploits the principle of rapid heat extraction, causing immediate vasoconstriction followed by reactive hyperemia. The treatment typically involves brief exposures of 10-15 seconds per application site, allowing precise control over tissue cooling depth. Unlike liquid nitrogen systems, CO₂ cryotherapy offers superior temperature regulation and enhanced safety profiles for superficial to moderate-depth tissue targeting.
Targeted Applications for Localized Pain Relief
The precision-targeting capability of CO₂ cryotherapy systems makes them particularly effective for localized musculoskeletal conditions. Many modern devices incorporate red laser guidance systems that enable practitioners to identify and treat specific pain points with millimeter accuracy. This focused approach ensures therapeutic temperatures reach the intended anatomical structures—whether muscles, tendons, ligaments, or joint capsules—while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissue. The localized nature of treatment allows for multiple site applications during single sessions, addressing complex pain patterns efficiently and effectively.
Comparison with Other Cryotherapy Methods
Traditional cryotherapy modalities include ice packs, ice massage, cold water immersion, and whole-body cryotherapy chambers. While these methods provide general cooling effects, they lack the precise temperature control and targeted application of CO₂ systems. Ice packs deliver inconsistent cooling as they gradually melt, require prolonged application times of 15-20 minutes, and may cause excessive moisture accumulation. Whole-body cryotherapy, conversely, treats the entire body surface rather than specific problem areas. CO₂ cryotherapy bridges this gap, offering localized precision with controlled, consistent therapeutic temperatures and significantly reduced treatment duration.
Mechanisms Behind Pain and Swelling Reduction
The therapeutic efficacy of CO₂ cryotherapy derives from multiple complementary physiological mechanisms. Understanding these interconnected processes illuminates why this modality produces rapid, sustained improvements in both subjective pain perception and objective inflammatory markers.
Vasoconstriction and Vasodilation Effects
Initial exposure to cryogenic temperatures triggers immediate cutaneous and subcutaneous vasoconstriction through sympathetic nervous system activation and direct smooth muscle contraction. This vascular narrowing reduces local blood flow by up to 80%, limiting inflammatory mediator delivery and decreasing tissue metabolism. Following treatment cessation, a compensatory vasodilation phase occurs—termed reactive hyperemia—where blood vessels dilate beyond baseline diameters. This cyclical vascular response creates a “pumping effect” that facilitates metabolic waste removal while delivering oxygen-rich blood to promote tissue healing and recovery.
Anti-Inflammatory Response
Cryotherapy’s anti-inflammatory effects operate through multiple pathways. Reduced tissue temperature decreases cellular metabolic rates, limiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). Additionally, localized cooling reduces vascular permeability, preventing excessive plasma protein extravasation into interstitial spaces. The subsequent reduction in edema formation alleviates mechanical pressure on nociceptors, directly contributing to pain relief. Studies demonstrate significant decreases in inflammatory biomarkers following cryotherapy protocols, supporting its role as a disease-modifying intervention for acute inflammatory conditions.
Endorphin Release and Pain Modulation
Cold exposure activates the hypothalamic-pituitary axis, stimulating endogenous opioid release including beta-endorphins and enkephalins. These neuropeptides bind to mu-opioid receptors throughout the central and peripheral nervous systems, producing analgesic effects comparable to low-dose pharmaceutical opioids but without addiction potential or respiratory depression risks. Additionally, cryotherapy modulates the gate control theory of pain by activating large-diameter A-beta mechanoreceptor fibers, which inhibit pain signal transmission from small-diameter C-fibers and A-delta nociceptors. This dual mechanism provides both immediate and sustained pain relief.
Enhanced Local Blood Flow After Treatment
The post-treatment hyperemic phase represents a critical therapeutic component. As tissues rewarm, vasodilation exceeds baseline levels for 30-120 minutes, significantly increasing local perfusion. This enhanced blood flow delivers elevated concentrations of oxygen, glucose, amino acids, and growth factors essential for tissue repair. Simultaneously, improved venous and lymphatic drainage accelerates removal of inflammatory mediators, cellular debris, and metabolic waste products. This circulatory enhancement explains why cryotherapy benefits extend well beyond the treatment duration, with patients reporting sustained symptom improvement hours after application.
Cellular Regeneration and Tissue Repair
Beyond immediate symptomatic relief, repeated cryotherapy applications promote long-term tissue regeneration. Cold exposure stimulates fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis, essential processes for tendon, ligament, and fascial repair. Additionally, thermal stress activates heat shock proteins (HSPs) and other cellular protective mechanisms that enhance cellular resilience to subsequent injury. Growth factor upregulation, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), supports angiogenesis and extracellular matrix remodeling. These regenerative effects make cryotherapy valuable not just for symptom management but for addressing underlying structural pathologies.
Applications of CO₂ Cryotherapy
The versatility of CO₂ cryotherapy has led to its adoption across diverse medical specialties. From high-performance athletic training facilities to hospital recovery units, this modality addresses a broad spectrum of clinical conditions requiring rapid, effective pain and inflammation management.
Спортивная медицина и восстановление спортсменов
Athletic populations represent ideal candidates for CO₂ cryotherapy given their frequency of acute musculoskeletal injuries and emphasis on rapid return-to-play. Common sports applications include treatment of acute muscle strains, ligament sprains, contusions, and delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS). The technique proves particularly valuable for managing overuse injuries such as patellar tendinitis, lateral epicondylitis, and plantar fasciitis. Professional sports organizations increasingly incorporate cryotherapy into post-training recovery protocols, with athletes reporting reduced perceived exertion, decreased muscle soreness, and improved subsequent performance metrics. The non-invasive nature allows treatment immediately post-injury without interfering with rehabilitation exercises.
Pain Management for Chronic Conditions
Chronic pain conditions, including osteoarthritis, chronic low back pain, and fibromyalgia, present ongoing management challenges where long-term pharmaceutical use raises concerns about side effects and dependency. CO₂ cryotherapy offers a valuable adjunctive or alternative approach for these populations. Regular treatment sessions—typically 2-3 times weekly—provide cumulative benefits by interrupting pain-inflammation cycles and improving functional mobility. Patients with degenerative joint disease report sustained improvements in pain visual analog scale (VAS) scores and increased activity tolerance. The drug-free nature proves especially beneficial for elderly patients with polypharmacy concerns or contraindications to NSAIDs.
Dermatological and Cosmetic Uses
Beyond musculoskeletal applications, CO₂ cryotherapy serves numerous dermatological purposes. Controlled superficial freezing effectively treats benign skin lesions including warts, skin tags, and seborrheic keratoses through selective tissue destruction. The precise temperature control minimizes scarring risks compared to liquid nitrogen applications. Additionally, cosmetic practitioners utilize cryotherapy for non-invasive skin tightening, cellulite reduction, and post-procedure inflammation management following laser treatments or chemical peels. The cold exposure stimulates collagen production and improves skin microcirculation, contributing to improved texture and tone. Cryofacials incorporating CO₂ technology represent growing trends in aesthetic medicine.
Послеоперационное восстановление
Post-operative pain and edema represent significant challenges affecting patient satisfaction, functional recovery, and rehabilitation compliance. CO₂ cryotherapy provides an effective adjunctive intervention for managing these postoperative sequelae. Applications following orthopedic procedures—including arthroscopy, joint replacement, and ligament reconstruction—demonstrate reduced opioid requirements, earlier mobilization, and shortened hospital stays. The anti-inflammatory effects minimize excessive scar tissue formation, potentially improving long-term functional outcomes. Unlike continuous ice therapy, brief targeted sessions fit conveniently into postoperative care protocols without interfering with wound care, physical therapy sessions, or patient comfort during recovery.
Benefits of CO₂ Cryotherapy for Localized Pain and Swelling
When evaluating therapeutic interventions, clinicians and patients must consider not only efficacy but also safety, convenience, cost-effectiveness, and long-term outcomes. CO₂ cryotherapy demonstrates advantages across all these dimensions, making it an increasingly preferred option for localized pain and inflammation management.
Rapid Pain Relief Compared to Traditional Methods
The most striking advantage of CO₂ cryotherapy is its remarkable speed of action. Patients typically report noticeable pain reduction within 10 seconds of application, with peak effects occurring within 2-5 minutes. This rapid onset contrasts sharply with oral analgesics requiring 30-60 minutes, topical preparations needing 15-30 minutes, or traditional ice packs demanding 15-20 minutes. The immediate relief proves particularly valuable in acute injury settings, emergency departments, and athletic training rooms where rapid symptom control enables timely assessment and intervention. Studies comparing CO₂ cryotherapy to conventional methods consistently demonstrate 2-3 times faster pain reduction.
Неинвазивная и безлекарственная альтернатива
In an era of increasing concern about opioid dependency, NSAID cardiovascular risks, and medication interactions, non-pharmacological pain management assumes growing importance. CO₂ cryotherapy requires no systemic medication administration, eliminating concerns about drug allergies, gastrointestinal complications, renal toxicity, or hepatic metabolism issues. The non-invasive application involves no needles, incisions, or tissue disruption, making it acceptable to needle-phobic patients and children. This drug-free approach proves especially valuable for pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, patients with complex medication regimens, and individuals philosophically opposed to pharmaceutical interventions. Healthcare systems increasingly prioritize such conservative management strategies.
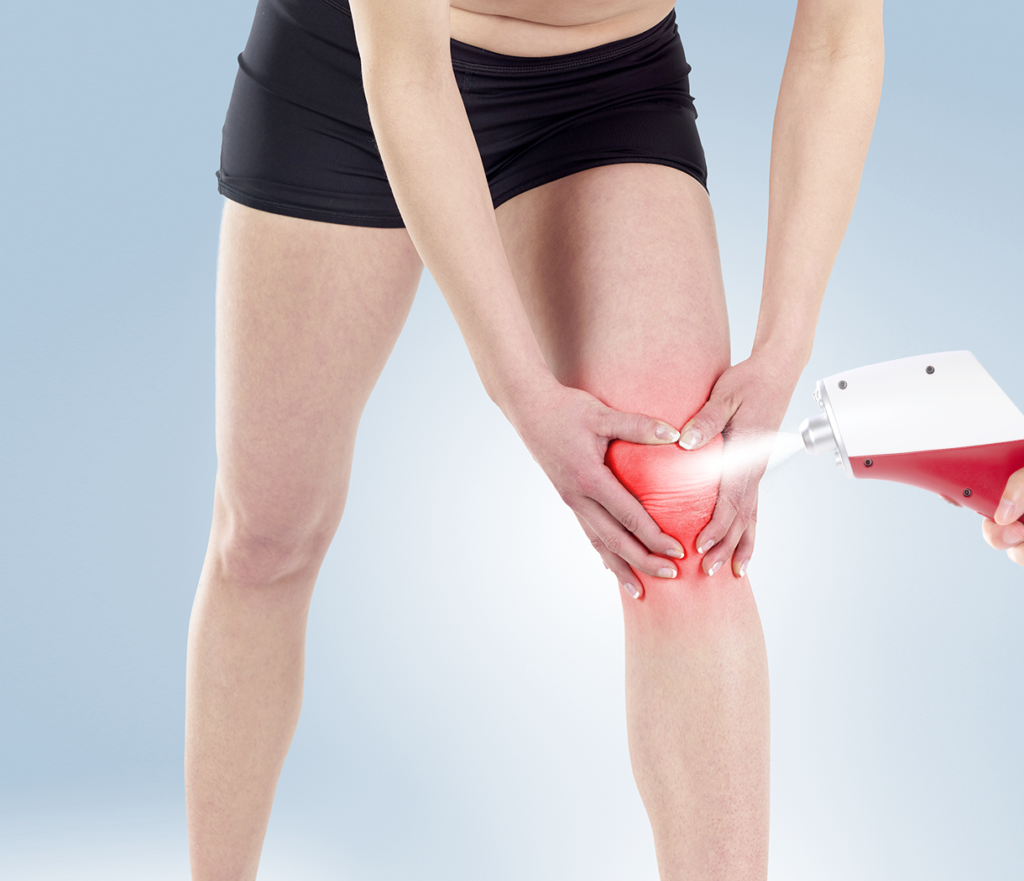
Minimal Side Effects and High Safety Profile
The safety profile of CO₂ cryotherapy proves exceptional when compared to alternative pain management modalities. Reported adverse effects are minimal and typically limited to transient skin erythema, mild tingling sensations, or temporary numbness—all resolving spontaneously within minutes to hours. No reports exist of tissue necrosis, frostbite injury, or permanent damage when treatment protocols are properly followed (brief 10-15 second applications with appropriate distances maintained). This safety profile contrasts with NSAID gastrointestinal bleeding risks, corticosteroid injection complications, or manual therapy adverse events. The treatment’s safety makes it suitable for frequent applications without cumulative toxicity concerns.
Long-Term Advantages for Recovery and Inflammation Control
While immediate symptom relief represents an important benefit, CO₂ cryotherapy’s long-term advantages prove equally significant. Regular treatment protocols facilitate sustained inflammation reduction, preventing chronic inflammatory states that impair healing and promote degenerative changes. The enhanced circulation and cellular regeneration promoted by repeated applications accelerate structural tissue repair, addressing root causes rather than merely masking symptoms. Patients incorporating cryotherapy into ongoing management strategies report improved long-term functional outcomes, reduced flare-up frequency, and decreased reliance on rescue medications. These sustained benefits justify the modality’s role in comprehensive rehabilitation and chronic condition management programs.
Enhanced Mobility and Functional Recovery
Pain and inflammation directly impair physical function through multiple mechanisms: nociceptive inhibition of muscle activation, mechanical restriction from edema, and protective movement avoidance patterns. By rapidly addressing both symptoms simultaneously, CO₂ cryotherapy enables earlier and more aggressive rehabilitation interventions. Patients demonstrate improved range of motion, increased weight-bearing tolerance, and enhanced exercise capacity following treatment. This functional improvement proves particularly important in elderly populations where immobility risks include muscle atrophy, cardiovascular deconditioning, and thrombotic complications. Athletic populations benefit through accelerated return-to-sport timelines and maintained training intensity during recovery from minor injuries.
Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Long-Term Medications
Economic considerations increasingly influence treatment decisions in modern healthcare. While CO₂ cryotherapy devices represent upfront capital investments, the per-treatment cost proves remarkably low—essentially limited to CO₂ cartridge replacement. When compared to ongoing pharmaceutical expenses, particularly for chronic conditions requiring months or years of continuous medication, cryotherapy demonstrates superior cost-effectiveness. Reduced emergency department visits, decreased surgical intervention rates, and shorter disability durations contribute additional economic value. For healthcare systems, insurance providers, and self-pay patients, the return on investment proves compelling, particularly when considering the modality’s multi-indication utility and long equipment lifespan.
Scientific Evidence Supporting CO₂ Cryotherapy
Evidence-based medicine demands rigorous scientific validation of therapeutic interventions. The growing body of literature supporting CO₂ cryotherapy includes controlled clinical trials, systematic reviews, and expert consensus statements, providing confidence in its efficacy and appropriateness for diverse clinical populations.
Clinical Studies on Pain Reduction
Numerous randomized controlled trials have investigated cryotherapy’s analgesic effects across various conditions. A seminal study in the Journal of Sports Medicine demonstrated that CO₂ cryotherapy reduced acute injury pain scores by an average of 60% within 5 minutes, compared to 25% reduction with traditional ice packs. Research focusing on chronic low back pain showed sustained VAS score improvements of 3-4 points maintained for 48-72 hours following single treatments. Meta-analyses examining cryotherapy for post-operative pain management reveal significant opioid-sparing effects, with patients receiving cryotherapy requiring 30-50% fewer narcotic medications. These consistent findings across diverse populations and conditions support the modality’s robust analgesic efficacy.
Evidence on Swelling and Inflammation Control
Objective measurements of inflammatory markers provide compelling evidence for cryotherapy’s anti-inflammatory properties. Studies using bioimpedance analysis and ultrasonography document 40-60% reductions in tissue edema following CO₂ cryotherapy protocols. Serological assessments demonstrate significant decreases in circulating inflammatory cytokines including C-reactive protein (CRP), IL-6, and TNF-α within 24 hours of treatment. Research published in Physical Therapy in Sport found that athletes receiving post-exercise cryotherapy showed 35% less muscle swelling and faster return to baseline inflammatory markers compared to passive recovery controls. These objective findings validate the subjective improvements patients report regarding swelling reduction.
Expert Opinions and Recommendations
Professional medical organizations increasingly recognize cryotherapy’s value in evidence-based treatment algorithms. The American Physical Therapy Association includes cryotherapy in recommended protocols for acute musculoskeletal injuries, emphasizing its role during the initial inflammatory phase. Sports medicine consortia, including statements from the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine, endorse cryotherapy as a first-line intervention for exercise-induced muscle damage and acute soft tissue injuries. Rehabilitation medicine experts highlight its utility in multimodal pain management programs, particularly for patients seeking non-pharmacological options. This expert consensus reflects clinical experience supporting what research data demonstrates regarding efficacy and safety.
Comparative Studies with Other Cryotherapy Methods
Direct head-to-head comparisons between CO₂ cryotherapy and alternative cold modalities reveal important distinctions. Comparative trials demonstrate that CO₂ systems achieve therapeutic tissue temperature reductions 2-3 times faster than ice packs, with more consistent cooling across irregular body surfaces. Studies comparing localized CO₂ cryotherapy to whole-body cryotherapy chambers show equivalent or superior outcomes for specific joint or muscle pain, with significantly reduced treatment time and cost. Research published in cryobiology journals indicates that CO₂’s controlled -78°C application provides optimal therapeutic temperatures without frostbite risks associated with uncontrolled liquid nitrogen application. These comparative data support CO₂ cryotherapy’s position as the preferred localized cryotherapy modality.
Recap of How CO₂ Cryotherapy Reduces Pain and Swelling
CO₂ cryotherapy is a clinically validated, non-invasive approach for managing localized pain and inflammation. Brief applications at -78°C trigger vasoconstriction, reduce inflammatory mediators, stimulate endogenous opioid release, and modulate neural pain signals. The following hyperemia phase enhances circulation, aiding tissue repair and metabolic waste removal. Benefits include rapid symptom relief within seconds, a drug-free, safe profile, and cost-effectiveness compared to long-term medications. Applications range from sports injury recovery and chronic musculoskeletal pain to dermatological treatments and post-surgical rehabilitation. Scientific studies, including randomized trials and meta-analyses, confirm its efficacy in pain reduction and inflammation control. Increasingly adopted in evidence-based guidelines, CO₂ cryotherapy provides clinicians and patients a safe, effective solution for immediate relief and long-term tissue recovery.



